High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer produced from the monomer ethylene. Known for its exceptional strength-to-density ratio, it stands as one of the most widely used plastics in the world, valued for its durability, chemical resistance, and versatility. From robust underground piping systems to food-grade containers, HDPE is the backbone of modern manufacturing.
Finding a reliable source for high-quality polyethylene is critical for industrial success. Shobeir Shimi Company is a premier supplier of High Density Polyethylene, offering a comprehensive portfolio of grades—including Injection, Blow Molding, Film, and Pipe (PE100/PE80). We bridge the gap between top-tier petrochemical producers and global manufacturers, ensuring consistent quality, competitive pricing, and seamless export logistics.
Why HDPE is the Material of Choice?
The demand for HDPE continues to grow globally because it offers a unique combination of properties that few other materials can match. It is:
- Structurally Strong: Its linear molecular structure allows for high crystallinity, making it tougher and more rigid than LDPE.
- Chemically Inert: It resists degradation from acids, solvents, and cleaning agents, making it ideal for chemical storage.
- Sustainable: HDPE is 100% recyclable (Resin Code #2), supporting the global shift towards eco-friendly production.
Whether you are manufacturing pressure pipes that must last 50 years or lightweight packaging for consumer goods, our extensive inventory ensures you receive the exact technical grade required for your production line.
What Is HDPE?
Technically, HDPE is low-branched linear polyethylene, which is of low branching and could be described as High Density polyethylene resin as it is offered in pellet form. The question that customers may ask is, “what is high density polyethylene (HDPE)”? The answer is a high-strength, semi-crystalline thermoplastic utilized in the entire world as pipes, packaging, structural parts, and films due to its terrific combination of mechanical performance, processability, and cost.
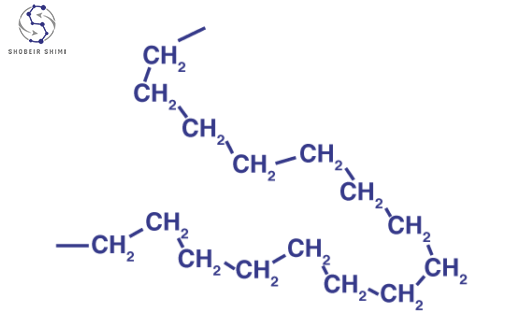
HDPE Chemical Formula & Structure
The HDPE formula, or chemical formula for HDPE, is (C2H4)n(C2H4)n, the same high-density polyethylene formula that is used to explain a long chain or repeating ethylene units with a minimal number of side branches. This linear molecular structure enables the chains to be packed very densely thereby making them more crystalline and densified, which leads directly to an improvement in stiffness, tensile strength, and chemical resistance, important HDPE characteristics in engineering or packaging use.
HDPE Density Values
The density of the HDPE (High-density polyethylene) falls within 930-970 kg / m3 (0.93-0.97 g/cm3), though the variations depend on the grade and the method used in its processing. Direct conversion of kg/m 3 to g/cm 3 is::
- 1 g/cm3=1000 kg/m31 g/cm3=1000 kg/m3
- Divide the kg/m³ value by 1000 to get g/cm³.
| Grade Category | Density (kg/m³) | Application Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Standard/General HDPE | 930–970 | General Purpose |
| High crystallinity | 961 | Rigid Packaging |
| Common engineering | 940–955 | Structural Parts |
| Pipe Grades (PE100) | 0.955 – 0.960 | High-Pressure Pipes |
Density Variation by Grade
Because of molecular structure, i.e. the level of crystallinity and chain branching, the density of HDPE changes. Less branching and higher crystallinity grades contain closer-packed chains, and this means that they are denser and have better mechanical strength. These variations are also caused by processing technique, molecular weight, and additives.
Influence of Density on Properties
- Stiffness: An increase in density tends to increase stiffness and rigidity, and consequently, HDPE is preferred as a load-bearing material or a structural one.
- Toughness/Impact Resistance: Toughness and impact resistance of HDPE decrease slightly with an increase in density, but its strength and dimensional stability increase.
- Processing: The lower-density materials tend to be easier to process and more flexible and elongating, whereas higher-density HDPE could need closer attention to the melt temperature and cooling rates to achieve the best outcomes.
The density as well as the balance between strength, stiffness, and impact performance of the material are not only dictated by the molecular arrangement and the method of processing, but also the final product is directed to end-use applications.
what are the properties of high density polyethylene (HDPE)?
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) is distinguished from other polymers by its linear molecular structure and low branching. This unique architecture results in a highly crystalline material that offers an exceptional balance of rigidity, toughness, and chemical inertness.
For manufacturers, understanding these properties is essential for selecting the right grade. Shobeir Shimi supplies HDPE resins that adhere to strict international standards (ASTM/ISO), ensuring consistent performance across all critical parameters.

1. Physical and Mechanical Strength
HDPE is renowned for its high strength-to-density ratio. With a density range of 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm³, it is lightweight yet incredibly strong.
- Tensile Strength: It can withstand high tensile loads without breaking, making it ideal for pressure pipes (PE100/PE80) and geomembranes.
- Impact Resistance: HDPE exhibits excellent resistance to impact, even at low temperatures. It does not shatter easily, which is vital for blow-molded containers like fuel tanks or industrial drums.
- Stiffness: It is stiffer than Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) and Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE), providing structural integrity for crates and pallets.
2. Chemical and Environmental Resistance
One of the primary reasons industries choose HDPE is its chemical stability.
- Chemical Inertness: It is highly resistant to a wide range of strong acids, alkalis, salt solutions, and organic solvents. This makes it the material of choice for detergent bottles and chemical storage tanks.
- ESCR (Environmental Stress Crack Resistance): High-quality HDPE grades (especially blow molding types) are formulated to resist cracking when exposed to surface-active agents (like soaps), ensuring the longevity of packaging.
- Moisture Barrier: HDPE has extremely low moisture absorption, effectively acting as a waterproof barrier.
3. Thermal Properties
HDPE performs reliably across a broad temperature spectrum.
- Melting Point: With a typical melting point between 120°C and 135°C, it remains solid and rigid at higher temperatures compared to LDPE.
- Low-Temperature Toughness: Uniquely, HDPE retains its flexibility and impact strength even in freezing conditions (down to -60°C), making it suitable for freezer-grade packaging and outdoor piping in cold climates.
HDPE Properties Table
Below is a summary of the typical properties for commercial HDPE grades available through Shobeir Shimi. Please note that specific values vary by grade (Injection, Blow, Film, etc.).
Need a specific Datasheet?
Different applications require different technical specifications. Whether you need a high-flow grade for injection molding or a high-ESCR grade for bottles, we can provide the exact Technical Data Sheet (TDS) for products from Jam, Arya Sasol, and other top producers. Contact Our Technical Team
HDPE Grades, Granules, & Resin Supply
Commercial buyers usually begin with grade selection, as the right HDPE grades determine product performance. Our HDPE supply includes:
- HDPE Film Grades (HF, HM Series): It finds application in high-performance films, grocery bags, industrial liners, as well as agricultural sheeting.
- HDPE Blow Molding Grades (HBM Series): Best suited for bottles, drums and containers that require high levels of stress crack resistance.
- HDPE Injection Molding Grades (e.g., 52518, EX): Provides automobile components, caps, toys, and rigid packaging.
- HDPE Pipe Grades (PE80, PE100): Pipes are required to handle the pressure of water, gas, and sewage systems.
- Rotomolding Grades & High-Flow Specialty Grades: Specialty grades aimed at tanks, playground systems and custom large molded parts.
The choice of HDPE grade is an important issue: the performance, processability and product life strongly depend on the choice of grade. Our website features high demand, trending HDPE film, pipe and injection grades, always supported with complete HDPE datasheet information.
HDPE injection molding grade is used to produce rigid, high-strength plastic products through an injection process. This grade is commonly used in the manufacturing of plastic crates, containers, housewares, industrial parts, and medical equipment. Injection-molded HDPE has excellent impact resistance, making it suitable for automotive components, caps, closures, and storage bins.
| GRADE | PRODUCER | MFR (190°C / 2.16kg ) | DENSITY (g/cm3) | DATASHEET |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 52518 | JAM | 18 | 0.954 | |
| 60505UV | JAM | 5 | 0.952 | |
| 60507UV | JAM | 7.5 | 0.958 | |
| 60511 | JAM | 11 | 0.958 | |
| 52B07 | LORESTAN | 7 (5K/G) | 0.952 | |
| 52505UV | jam | 5 | 0.952 | |
| I3 | AMIRKABIR, KERMANSHAH | 8 (5K/G) | 0.957 | |
| 2200J | ILAM | 5.8 (5K/G) | 0.953 | |
| 52B18 | LORESTAN | 18 | 0.952 | |
| 62107UV | LORESTAN | 7 (5K/G) | 0.962 | |
| 5030SA | TABRIZ | 2 | 0.950 | |
| 5218EA | TABRIZ | 18 (5K/G) | 0.952 | |
| 5218UA | TABRIZ | 18 (5K/G) | 0.952 | |
| 6040UA | TABRIZ, LORESTAN | 3.6 (5K/G) | 0.960 | |
| 6070UA | TABRIZ | 7.2 (5K/G) | 0.960 | |
| HD62N18 | BAKHTAR | 15-21 (5K/G) | 0.960-0.964 | |
| HD62N07 | BAKHTAR | 6-8 (5K/G) | 0.960-0.964 | |
| HD52B18 | BAKHTAR | 18 | 0.952 | |
| 54B04 UV | BAKHTAR | 3.6-4.4 | 0.952-0.956 | |
| 52511 | JAM | 11 | 0.952 | |
| HI0500 | BANDAREMAM | 5 | 0.965 | |
| 5620EA | ARAK | 20 | 0.956 | |
| 54B04 | LORESTAN | 3.6-4.4 | 0.952-0.956 | |
| HD7260 | BAKHTAR | 23±3 | 0.957±0.002 | |
| I4 | AMIRKABIR, MARUN | 4.0 ± 0.7 | 0.954 ±0.002 | |
| HD3840UA | LORESTAN, TABRIZ | 3.6-4.4 | 0.935-0.939 | |
HDPE blow molding grade is specifically designed for making hollow plastic products, such as bottles, jerry cans, and drums. It offers good stress crack resistance, impact strength, and lightweight properties, making it ideal for packaging applications in food, beverage, pharmaceutical, and household chemicals. Blow-molded HDPE is also used in automotive fuel tanks due to its resistance to chemicals and durability.
| GRADE | PRODUCER | MFR (gr/10min) | DENSITY (gr/cm3) | DATASHEET |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL3 | JAM | 1.2±0.3 | 0.954±0.002 | |
| HD4760 | BAKHTAR | 1 | 0.954 | |
| 0035 | BANDAREMAM | 0.35 | 0.959 | |
| BL4 | JAM, AMIRKABIR, KERMANSHAH | 0.29-0.41 | 0.949-0.953 | |
| 5510 | ARYA SASOL | 0.075 | 0.955 | |
| HD4750 | BAKHTAR, KERMANSHAH | 1.1+0.3 | 0.944+0.002 | |
| HD52HF2 | BAKHTAR | 0.18+0.22 | 0.950-0.954 | |
| HBM 4265 | Arya Sasol | 6.5 | 0.942 | |
| HBM 5520 | Arya Sasol | 0.25 | 0.955 | |
| HBM 5020 | Arya Sasol | 0.3 | 0.950 |
HDPE rotational molding grade is used in large, seamless, and durable plastic products. This process creates uniform, stress-free structures with excellent impact resistance. Common applications include storage tanks, playground equipment, traffic barriers, and outdoor furniture. Rotomolded HDPE is preferred for large, custom-molded items due to its ability to form thick, sturdy walls without weak points.
HDPE film grade is a thin, flexible type of polyethylene used for plastic bags, agricultural films, food packaging, and liners. It provides moisture resistance, durability, and lightweight performance while maintaining excellent tensile strength. HDPE films are widely used in the packaging industry, particularly for grocery bags, produce bags, and industrial liners. Some specialized HDPE films also have UV stabilization for outdoor use.
HDPE caps and closures grade is used to manufacture plastic lids, bottle caps, and tamper-evident closures. This grade has high stiffness, dimensional stability, and excellent sealing properties, making it ideal for beverage, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic containers. Due to its chemical resistance, it is widely used in detergent and chemical packaging as well.
HDPE Pipe Grades are specifically formulated to meet the rigorous demands of modern water, gas, and sewage piping systems. These high-performance polyethylene resins offer an exceptional combination of properties, making them an indispensable choice for critical infrastructure projects.
| GRADE | PRODUCER | MFR | DENSITY | DATASHEET |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7700M | KHALIJE FARS, ILAM | 0.27 | 0.949 | |
| HMCRP 100 BLACK | JAM | 0.20-0.24 | 0.955-0.959 | |
| PE100 | JAM | 0.19-0.25 | 0.946-0.950 | |
| PE80 | ARYA SASOL | 0.33 | 0.944 | |
| EX3 | JAM, MARUN | 0.39-0.51 | 0.943-0.947 | |
| PCF55 | SHAZAND | 22.8 | 0.959 | |
| 4440EA | TABRIZ | 4 | 0.944 |
To manufacture HDPE pipes, raw polyethylene is dried, heated to approximately 180 °C (356 °F), and extruded through a die. The pipes are often black due to the addition of carbon black, which enhances UV resistance. After cooling, the pipes are printed with relevant information and cut to the desired lengths. HDPE pipes are utilized in a variety of applications, including water supply, sewerage and drainage, and gas distribution. They are safe for transporting potable water due to the use of food-grade polyethylene and are commonly used in sewage systems and stormwater management due to their chemical resistance. They are also suitable for high-pressure gas mains, making them a versatile and reliable choice for many industries.
HDPE raffia grade is primarily used in woven plastic products, such as woven sacks, ropes, straps, and tarpaulins. This grade provides high tensile strength, durability, and weather resistance, making it suitable for agriculture, construction, and industrial packaging. HDPE raffia is widely used in grain storage bags, cement bags, and bulk packaging materials due to its superior tear resistance and flexibility.
Typical uses of HDPE raffia in woven fabrics include:
- Agriculture: Crop covers, shade nets
- Packaging: Durable bags
- Construction: Tarpaulins, scaffolding nets
- Industrial settings: Conveyor belts, sacks
Its strength and durability ensure that HDPE raffia remains reliable across these diverse applications.
HDPE Density: kg/m³ & g/cm³
Comparing HDPE datasheets, you will notice that the typical range of HDPE density kg/m3 is between 930-970 kg/m3, and the range of HDPE density g/cm3 is between 0.93- 0.97 g/cm3. This is very compact due to the linear polymer structure of HDPE (PE high density), which reduces branching to allow the highest packing density. Density influences not only the stiffness and toughness of materials but also the ways of processing many products of HDPE film to high density polyethylene, and a variety of industrial pipes.
HDPE Granules – Virgin, Industrial & Food-Grade
The Virgin HDPE granules are directly produced out of the petrochemical refineries in order to provide the highest level of purity and consistency in highly sensitive technical and food contact applications.
We are one of the trusted HDPE granules suppliers providing high-quality virgin HDPE granules (not recycled), ideal for sensitive uses like food packaging, medical devices, and export. Our stock covers:
- HDPE plastic granules are suitable for film, pipe, blow molding, and extrusion.
- Bulk purchasing for manufacturers who need to buy HDPE granules in large quantities.
- Multiple packaging options (25 kg bags, jumbo bags) for easy logistics.
- Full batch certification and quality control across all supplies.
Our expansive network includes reliable HDPE granule suppliers, HDPE resin suppliers, and specialists in both industrial and food-grade HDPE for every business need. Contact us in Shobeir Shimi to consult and place your order.
HDPE 2 Recycling Code
HDPE is instantly recognizable by its HDPE 2 recycling code, which confirms authenticity and recyclability to global buyers and sustainability managers. This hallmark allows HDPE products to be safely reused and repurposed with minimal environmental impact.
HDPE Supplier & Global Export Capabilities
Sober Shimi is well known as a leading HDPE supplier, HDPE material supplier and HDPE resin supplier, offering direct sourcing and fast transactions for clients worldwide. Bulk HDPE supply is available for Asia, Africa, CIS, and Europe with full export certification (COA, MSDS, packing list, certificate of origin). Logistics are streamlined through Middle East ports for competitive pricing and reliable, on-time delivery.
Why Choose Our High Density Polyethylene Materials?
There are some reasons to choose Shobeir Shimi for Polyethylene materials:
- Direct access to high-density polyethylene suppliers and premium HDPE granule supplier partners.
- Consistent HDPE material specifications and superior batch quality.
- Comprehensive technical support with every order, including detailed HDPE datasheet documentation.
- Options for long-term supply contracts supported by on-time shipments and stable pricing.
We have strength in prompt delivery, extended supply agreements and stability in prices and values that create credibility in the long term with clients worldwide. We provide confidence on an enduring basis, whether you are looking to purchase HDPE granules, develop long-term procurement relationships, or need a large quantity of HDPE. Contact us now to consult and place your order.
Ready to Buy HDPE Granules or Resin?
Explore our current listings and reach out to our customer service team to buy HDPE granules in virgin, food-grade, or industrial variants. Whether you need high density polyethylene film, bulk resin HDPE, or custom HDPE supply solutions, we can rapidly fulfill your demands as your dedicated HDPE supplier.
high density polyethylene uses
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE), a thermoplastic polymer, is widely valued for its strength, durability, UV resistance, and FDA compliance. The versatile HDPE plastic use spans multiple industries, making it essential for various consumer and industrial applications. Below are some common High Density Polyethylene uses.
1. Packaging
high density plastic is a preferred choice for bottles, rigid containers, and films used in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries. Its chemical resistance and recyclability make it ideal for milk jugs, detergent bottles, and food storage containers.


2. Toys
Due to its impact resistance and non-toxic properties, HDPE is commonly used in outdoor and children’s toys. It is durable enough to withstand rough handling while being safe for children.
3. Hoses and Caps
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is widely used in irrigation systems, water pipes, and bottle caps due to its chemical resistance and flexibility. It ensures long-lasting performance in agriculture, construction, and beverage packaging.


4. Films and Tarpaulins
HDPE is used to produce damp-proof construction films and packaging materials. These films provide moisture resistance and durability, making them ideal for industrial and household applications.
5. Cosmetic Bottles
HDPE is commonly found in shampoo, lotion, and cream bottles, offering lightweight and leak-proof packaging while maintaining FDA compliance for personal care products.


6. Cutting Boards
Due to its non-porous surface and food-safe properties, HDPE is widely used for cutting boards in commercial and home kitchens. It resists bacteria growth and is easy to clean.
7. Water and Chemical Tanks
HDPE is a top material for fabricated tanks, offering corrosion resistance against water, chemicals, and industrial liquids, making it perfect for chemical storage and water treatment facilities.


8. Playground Systems
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is used in outdoor and indoor playground structures, as it resists weathering, UV radiation, and physical impact, ensuring long-term durability in recreational areas.
9. Marine Construction
HDPE’s resistance to water and salt makes it an ideal choice for marine applications, including pile guards, dock bumpers, and boat components.


10. Orthotics and Prosthetics
HDPE is used in AFOs (Ankle-Foot Orthoses) and KAFOs (Knee-Ankle-Foot Orthoses) due to its lightweight and flexible properties, allowing for comfortable, customized medical devices.
11. Tank and Chute Linings
For light-duty industrial applications, HDPE is used to line tanks, chutes, and hoppers, reducing wear and enhancing material flow.


12. Outdoor Cabinetry and Furniture
HDPE is ideal for outdoor cabinetry and furniture due to its UV resistance, moisture resistance, and long lifespan, making it perfect for gardens and patios.
13. Piping Systems
HDPE is widely used in drinking water, sewage, and natural gas piping, offering leak-proof connections and resistance to chemicals, corrosion, and environmental stress.


14. Geomembranes
HDPE is used in hydraulic applications such as reservoir linings, canal liners, and containment barriers, ensuring leak prevention and environmental safety.
15. Landfill Liners
To prevent soil and groundwater pollution, HDPE is used in landfill liners, acting as a barrier against hazardous waste leakage.


16. Cable Insulation
HDPE is an excellent insulator for electrical cables, protecting wires from moisture, chemicals, and environmental wear, making it essential for power and communication industries.
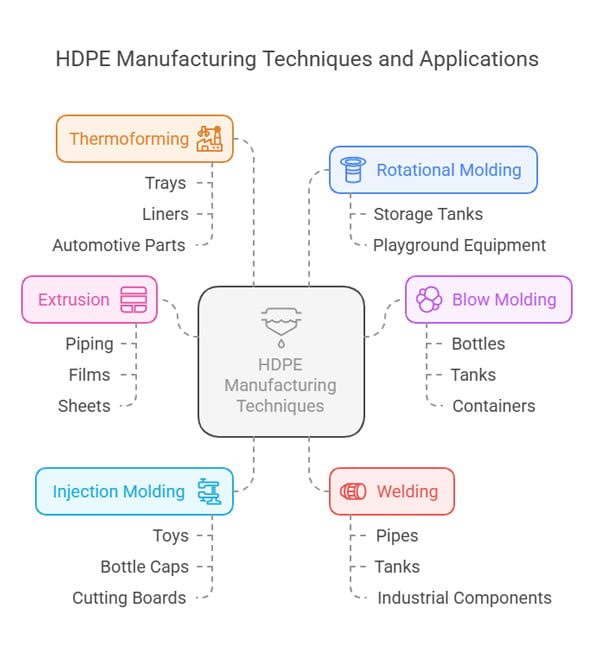
HDPE Processing and Manufacturing
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE), a thermoplastic polymer, is processed using various manufacturing techniques depending on its intended application. These methods ensure that HDPE retains its durability, UV resistance, and FDA compliance for safe use in food and medical industries.
- Extrusion: This method is used to produce constant–profile products such as piping, films, and sheets. Molten HDPE is forced through a die to create a continuous shape, making it ideal for water and gas pipes.
- Blow Molding: This process is used for making hollow plastic products like bottles, tanks, and containers. Air is blown into molten HDPE inside a mold, shaping it into a lightweight, recyclable
- Injection Molding: This technique forms complex, rigid parts such as toys, bottle caps, and cutting boards. Molten HDPE is injected into a mold under high pressure, producing durable, impact-resistant products.
- Rotational Molding: Used for creating large, seamless parts like storage tanks and playground equipment, this method involves slow rotation of a heated mold to evenly coat its interior with HDPE.
- Welding: HDPE parts can be joined using thermoplastic welding techniques, ensuring leak-proof connections in pipes, tanks, and industrial components.
- Thermoforming: This process involves heating High density polyethylene sheet and shaping them into trays, liners, and automotive parts. It allows for cost-effective mass production of lightweight yet strong products.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using HDPE
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a widely used thermoplastic polymer known for its strength, chemical resistance, and recyclability. However, like any material, it has both benefits and limitations.
Benefits of HDPE
- Strength and Durability: HDPE has a high strength-to-density ratio, making it ideal for pipes, tanks, and outdoor applications.
- Chemical Resistance: Due to its Hdpe chemical properties, it withstands exposure to acids, solvents, and industrial chemicals, making it a preferred material for packaging and chemical storage.
- Low Moisture Absorption: HDPE does not absorb water, ensuring longevity in marine and underground applications.
- Easy to Fabricate and Machine: It can be easily cut, welded, and molded into various shapes for custom applications.
- Weldability: Unlike some plastics, HDPE can be thermally welded, providing strong and leak-proof joints in piping and tanks.
- Recyclability: As an FDA-compliant material, HDPE is highly recyclable, reducing environmental impact.
- Recyclability: High density polyethylene examples such as bottles, bags, and containers are highly recyclable, reducing plastic waste.
- Cost-Effectiveness: HDPE is an affordable material compared to metals and some engineering plastics.
Disadvantages of HDPE
- Difficult to Bond with Adhesives: HDPE has low surface energy, making it hard to glue without special surface treatments.
- Difficult to Print or Paint: Traditional printing and painting do not adhere well, requiring surface modification.
- Difficult to Print or Paint: High-density polyethylene structure lacks natural adhesion for printing and painting, requiring specialized techniques.
- Not Suitable for High Temperatures: The High density polyethylene formula results in a material that softens at high temperatures, limiting its use in heat-intensive applications.
- Poor Dimensional Stability: It expands and contracts with temperature changes, affecting precision applications.
Recycling HDPE
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is one of the most commonly recycled plastics, identified by the resin identification code “2”. Its recyclability helps reduce plastic waste, minimize environmental impact, and lower the demand for new plastic production. Recycled HDPE is used in bottles, piping, plastic lumber, bins, and outdoor furniture. The recycling process involves collection, cleaning, shredding, and reprocessing into new products. Since HDPE retains its strength and durability after recycling, it is a sustainable choice for both industrial and consumer applications. By recycling HDPE, we can significantly reduce landfill waste and contribute to an eco-friendlier plastic economy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is a highly versatile and durable thermoplastic polymer known for its linear structure and minimal branching. This unique molecular arrangement results in a dense, crystalline material with exceptional mechanical strength, stiffness, and chemical resistance. Produced using advanced catalytic methods, HDPE’s properties make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from packaging and piping to automotive and construction materials. Its combination of high tensile strength, temperature resistance, and excellent chemical stability underscores its importance in various industrial and consumer products.






















