Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), or by other trade names like Styrofoam or white cork is a lightweight, closed-cell foam plastic item from the petroleum-based polymer polystyrene. It has 98% air and 2% solid content in its composition with a record degree of lightness, strength, and insulation characteristics. Such qualities make expanded polystyrene the most adaptable and cost-effective Polystyrene foam item throughout the whole world today.
Expanded Polystyrene is highly popular in its usage for packaging, construction, and insulation due to its shock-absorbing capabilities as well as its thermal resistance. As a rigid foam, it’s particularly effective in conserving energy within structures and protecting sensitive products throughout transport. Its applications span different industries, including civil engineering, automobiles, consumer products, and agriculture.
One of the outstanding advantages of Expanded polystyrene insulation is that it is remarkably durable and also resistant to rot, insect invasion, and moisture. Another advantage is that EPS can be recycled and thus becomes increasingly popular in an environmentally conscious world. Its relatively low production cost and availability have also made expanded polystyrene a material of choice in both developing and developed economies. With its unique combination of physical and environmental benefits, expanded polystyrene continues to be a significant element of modern building, packaging, and insulation technologies.
How is expanded polystyrene (eps) made?
EXPANDED POLYSTYRENE (EPS) production is a complex, multi-stage process by which microscopic polystyrene beads are transformed by heat, humidity, and pressure into light, durable foam products with an expansion factor of up to 50 times the volume of the original bead.
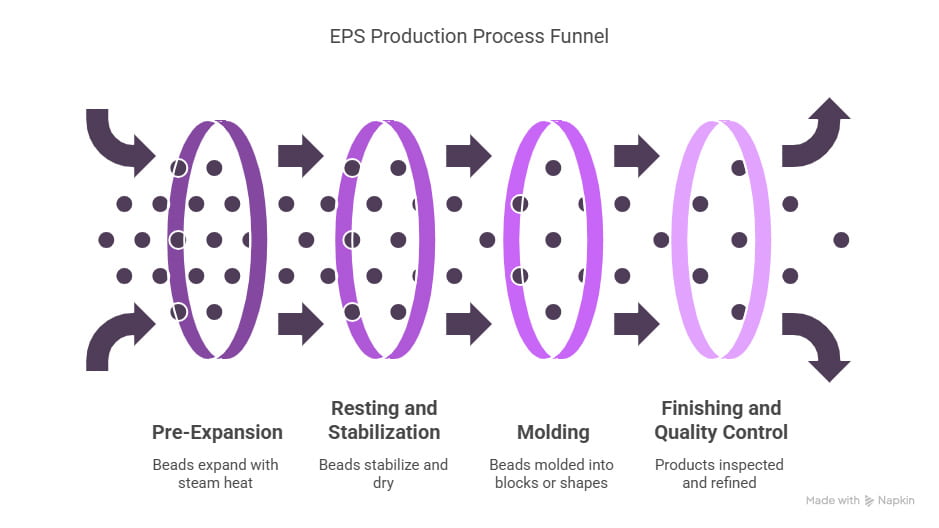
1. Pre-Expansion
The process is initiated from raw polystyrene beads that each contain a blowing agent (usually pentane) within. When exposed to steam heat, the beads become melted and expand as the evaporation of the blowing agent leaves small gas-full cells. The result is several times larger expanded beads than the original size. The expansion ratio at this point is a primary variable in maintaining the final Expanded Polystyrene density.
2. Resting and Stabilization
After pre-expansion, the beads are transported to a storage silo or fluidized bed, where they remain idle for 6 to 12 hours. The beads stabilize, reach equilibrium pressure, and evaporate surface moisture during this period.
3. Molding Process:
- Block Molding: In this process, stabilized beads are filled into large molds and steamed once more. These blocks can then be cut into sheets for applications in Expanded polystyrene insulation, packaging, and other uses.
- Shape Molding: For specialty applications in custom projects such as protective packaging or specialty building materials, pre-expanded beads are filled into pre-formed shapes.
This method allows user-specified shapes and components, supporting various applications in automotive parts, insulated containers, and architectural detailing.
4. Final Finishing and Quality Control
Once the molded products have cooled and hardened, they undergo density control and inspection to obtain uniformity. EPS manufacturers can modify characteristics like compressive strength, heat resistance, and thickness by controlling bead size, steam temperature, and pressure of the mold. The entire process of expanded polystyrene manufacturing is efficient and sustainable in character, there is minimal waste and more opportunities for Expanded polystyrene recycling. Recycling expanded polystyrene can be reused again as insulation panels, injection-molded items, or even raw beads for expansion.
In summary, the Expanded Polystyrene manufacturing process converts simple polystyrene beads into very functional foam products that meet the requirements of different markets—thanks to its versatile production, good insulation value (Expanded polystyrene eps r value), and custom-made attributes.
The Outstanding Properties of EPS: Why It’s a Material of Choice
Expanded Polystyrene is now among the most widely used and dependable materials across various industries due to its exceptional combination of physical and functional properties. Insulation, packaging, and large infrastructures are just a few examples of where the major characteristics of Polystyrene foam cannot be substituted. Following is a more detailed look at how and why expanded polystyrene is superior.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation: Superior Energy Efficiency
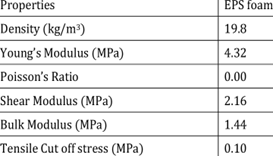
Among its main benefits are its outstanding thermal conductivity and R-value as a rating of resistance to thermal transmission. EPS R-value typically varies at around 3.6 to 4.2 per inch depending on structure and density and acts as extremely effective in energy consumption savings as well as retaining the heat.
This superior insulation quality has made Expanded Polystyrene widely employed in ventilated facades, ETICS systems (External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems), and prefabricated panels. It is also good at noise reduction, thereby suitable for domestic and commercial building acoustic comfort. In extremely warm or extremely cold climatic conditions, expanded polystyrene is heat stable, and thereby long-lasting efficiency and consistent energy saving can be guaranteed.
Lightweight and Easy to Handle: Facilitating Transportation and Installation
Due to its low density, EPS foam is extremely light, and that translates to ease of transport and cheaper shipping. Panels or blocks are easily handled by laborers with minimal effort, and that implies quicker and more efficient installation. Such ease of labor is most valuable in construction jobs where time and labor costs are the highest considerations.
Strength and Durability: Resistance to Adverse Conditions
Although light in weight, Expanded Polystyrene is mechanically strong and has compressive strength, typically between 70–250 kPa based on density. It can withstand loads without deforming, hence it is applicable for load-bearing applications like floor insulation and road construction. EPS also has shock absorption, which explains its widespread use in packaging fragile or delicate materials. Its ability to withstand humidity and harsh environmental conditions also makes it more resistant, extending the lifespan of materials and structures it transports with it.
Dimensional Stability: Long-Term Performance
Expanded Polystyrene exhibits higher dimensional stability with minimum change in form and shape in varying environmental conditions. It meets standards like ASTM D2126, which ensures temperature fluctuation resistance, moisture, and other conditions that otherwise cause deformation in low-quality material. The long-term stability ensures that EPS maintains its insulation performance and structural integrity for decades without the necessity of maintenance.
Cost-Effectiveness: Economical Solutions for Various Industries
Compared to other insulation and packaging materials, expanded polystyrene eps price is significantly lower in most cases. It is a low-cost product because its raw material price is cheap and its labor and transport costs are low. It provides affordable material alternatives for construction, manufacturing, agriculture, and logistics without compromising quality.
Design Flexibility: Adaptable to Diverse Applications
Expanded Polystyrene can be easily shaped into various sizes and forms due to its high moldability and tolerability. From building panels of large sizes to decorations, from intricate packaging inserts to building panels of huge sizes, Expanded polystyrene beads can be shaped almost into any form through block molding or shape molding. This allows expanded polystyrene to be used in standardized products or in tailor-made shapes, which facilitates innovative use in building and industrial design.
Chemical Inertness: Safe and Reliable
Expanded Polystyrene is not chemically reactive with most chemicals like acids, alkalis, and salts, and hence it can be utilized to pack food products and drug products. This chemical resistance also leads to its use in Expanded polystyrene in construction where exposure to other materials may be harmful to performance.
Water Resistance: Minimal Moisture Absorption
Expanded Polystyrene is water-repelling and will absorb zero moisture, maintaining its structural and insulating role even when used in wet environments. Such a feature ensures it for use in foundations, walls, and roofing where wetting or the presence of moisture is of concern. Its low water absorption ensures to prevention of decay and the growth of mold and mildew, contributing to improved indoor conditions.
Where is EPS Used? Exploring Its Wide Range of Applications
EXPANDED POLYSTYRENE is a highly adaptable material that has a multitude of applications across many different industries. From maximizing the energy efficiency of buildings to ensuring the safe packaging of fragile objects, expanded polystyrene Styrofoam or Polystyrene foam continues to prove useful as it has an ideal combination of high strength, low weight, and insulation.
Construction: Building a More Energy-Efficient World
One of the most powerful applications of EXPANDED POLYSTYRENE construction is as an advanced thermal insulation. Since it is closed-cell and possesses a firm Expanded polystyrene eps r value (typically between 3.6–4.2 per inch), expanded polystyrene is more effective than other insulating products such as foundation, floor, wall, and roof insulation.
EXPANDED POLYSTYRENE finds application in Insulated Concrete Forms (ICF) used for energy-efficient walls and foundations systems, Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) that are prefabricated panels with expanded polystyrene cores, and in External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems (ETICS) which involve improving building envelopes for energy conservation purposes. It is used in building construction as it helps enhance energy efficiency and helps in sustainability goals in the building sector since it reduces the heating and cooling loads in residential and commercial buildings.

Packaging EPS: Protecting Goods during Transportation
EPS is also widely applied in protective packaging on account of its superior shock resistance, cushioning, and lightweight. It is applied for protecting a broad spectrum of products in shipment and storage, including:
- Electronics and appliances: Impact damage prevention.
- Food packaging: Like expanded polystyrene trays, meat boxes, and fresh-keeping containers.
- Temperature-sensitive products: It maintains pharmaceuticals, seafood, and perishable goods at stable temperatures within isothermal containers and cold chain logistics.
Its void-fill ability also renders it most suited to oddly shaped packaging, and its light weight reduces the expense of overall shipping and fuel consumption.

Other Industries: Beyond Construction and Packaging
The unique characteristics of EPS—buoyancy, low weight, and formability—have brought it to serve in a chain of niche markets:
- Automotive Industry: Used on bumpers and interior components to provide added energy absorption and lightness for fuel efficiency enhancement.
- Marine and Flotation: Used to create buoyancy aids, piers, life jackets, and floating staging.
- Theatrical and Architectural Applications: Ideal for temporary architecture and stage sets due to ease of shaping and little weight.
- Food Service: Extensively used in disposable containers, cups, and trays.
- Agriculture: As coverings of plant protectants and seed trays.
Polystyrene density can also be formulated to satisfy some functional needs – ranging from hard and rigid to light and cushions – thereby making it a very versatile product.
Types of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Their Industrial Applications
Expanded Polystyrene is available in various forms, each designed for specific applications and performance requirements. The different types are classified according to density, fire resistance, and special properties to meet industry demands.
Classification by Density
EXPANDED POLYSTYRENE is primarily categorized by density, which directly influences its properties:
- Low-Density EPS (10-16 kg/m³): Used for general packaging and non-load-bearing insulation.
- Medium-Density EPS (16-25 kg/m³): Common in wall insulation and packaging for moderately heavy items.
- High-Density EPS (25-35 kg/m³): Provides enhanced compressive strength for floor insulation and load-bearing applications.
- Ultra-High-Density EPS (>35 kg/m³): Used in civil engineering projects and geofoam installations.
Fire-Rated EPS
For safety considerations, EPS is available in two main variants:
- Standard EPS: Basic grade without fire-retardant additives.
- Fire-Retardant EPS (FR-EPS): Contains additives that reduce flammability, mandated by building codes in many countries.
Specialized EPS Types
Several specialized variants offer enhanced properties:
- Graphite-Enhanced EPS: Contains graphite particles that improve thermal insulation by approximately 20%.
- Water-Resistant EPS: Specially treated for high-humidity environments and subgrade installations.
- Food-Grade EPS: Manufactured under strict hygiene conditions for food packaging and temperature-controlled shipping.
- Geofoam EPS: Engineered for geotechnical applications and lightweight fill material.
Manufacturing Methods
The production process creates two distinct types:
- Block-Molded EPS: Produced in large blocks that are cut into sheets or custom shapes.
- Shape-Molded EPS: Directly molded into finished shapes for custom packaging and components.
Composite EPS Products
Innovation continues with hybrid products:
- EPS Composites: Combines Expanded Polystyrene with materials like cement or fiber reinforcements.
- Sandwich Panels: Integrates EPS cores between facing materials like metal sheets or cement boards.
This variety allows professionals to select the precise material characteristics needed for specific applications while meeting energy efficiency and sustainability requirements.
| GRADE | PRODUCER | Bead Size (mm) | DENSITY | DATASHEET |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1000 | BANIAR | 1.2-2.0 | 12-13 | |
| F2000 | BANIAR | 0.8-1.2 | 13-15 | |
| F3000 | BANIAR | 0.4-0.9 | 15-17 | |
| F4000 | BANIAR | 0.3-0.5 | 17-19 | |
| P1000 | BANIAR | 1.4-2.0 | 10-11 | |
| P2000 | BANIAR | 0.9-1.4 | 11-13 | |
| P3000 | BANIAR | 0.7-1.0 | 13-15 | |
| P4000 | BANIAR | 0.5-0.8 | 15-17 | |
| SE 1000 | BANIAR | 1.2-2 | 20-21 | |
| SE 2000 | BANIAR | 0.8-1.2 | 21-23 | |
| SE 3000 | BANIAR | 0.4-0.9 | 23-25 | download |
| SE 4000 | BANIAR | 0.3-0.5 | 25-27 | download |
| HS 121 | TABRIZ | 1.8-2.5 | 13-15 | |
| HS 221 | TABRIZ | 1-1.8 | 14-30 | |
| HS 321 | TABRIZ | 0.7-1 | 18-30 | |
| 422FC | TABRIZ | 0.5-0.7 | 20-30 | |
| 522FC | TABRIZ | 0.3-0.5 | 22-30 | |
| 526WP | TABRIZ | 0.3-0.5 | — | |
| F50 | ENTEKHAB | — | 6-12 | download |
| F100 | ENTEKHAB | — | 7-12 | download |
| F200 | ENTEKHAB | — | 10-18 | download |
| F205 | ENTEKHAB | — | 13-20 | download |
| F300 | ENTEKHAB | — | 14-23 | download |
| F305 | ENTEKHAB | — | 15-23 | download |
| F400 | ENTEKHAB | — | ABOVE 20 | download |
| F405 | ENTEKHAB | — | ABOVE 21 | download |
| R100 | ENTEKHAB | — | 8-12 | download |
| R200 | ENTEKHAB | — | 12-20 | download |
| R220 | ENTEKHAB | — | 12-21 | download |
| R300 | ENTEKHAB | — | 13-25 | download |
| R310 | ENTEKHAB | — | 14-25 | download |
| R320 | ENTEKHAB | — | 14-25 | download |
| F40 | SHOBEIR | — | 5 – 15 | download |
| F50 | SHOBEIR | — | 10 – 20 | download |
| F100 | SHOBEIR | — | 14 – 22 | download |
| F150 | SHOBEIR | — | 16 – 30 | download |
| F250 | SHOBEIR | — | 20 – 35 | download |
| F350 | SHOBEIR | — | 22 – 40 | download |
| F450 | SHOBEIR | — | 23 – 42 | download |
The Sustainability of EPS: Recycling and Environmental Benefits
Even though Expanded Polystyrene has been criticized for being environmentally unsustainable, recent technology breakthroughs for recycling expanded polystyrene and green technologies are repositioning. It assists in contributing to energy efficiency, circular economy targets, and greenhouse gas emissions reduction when sustainably managed.
Recyclability of EPS: Contributing to a Circular Economy
Expanded Polystyrene is 100% recyclable. Post-consumer expanded polystyrene waste can be gathered, compacted, and recycled mechanically or chemically to be reused as new products in:
- Picture frames
- Office supplies
- New insulation materials
- Plastic lumber
Efforts are increasingly being made to recycle worldwide, with specialized EPS collection facilities and mobile compacting units making it increasingly possible.
Energy Efficiency and Reduced Carbon Footprint
One of the most important Expanded polystyrene uses is building insulation, which produces energy savings during the product’s lifetime. By minimizing heating and cooling needs, expanded polystyrene reduces CO₂ emissions, which helps to meet broader decarbonization goals within the construction industry.
Lightweighting and Transportation: Minimizing Environmental Impact
EPS’s low weight means reduced transportation costs, reduced fuel use, and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Compared to denser materials, expanded polystyrene significantly lowers the environmental impact of shipping goods and materials.
Non-Toxic and Safe: Environmental and Health Considerations
Expanded Polystyrene is chemically inert. It does not release toxic chemicals and does not contaminate food and therefore is safe for medical use and for food packaging. Expanded polystyrene, although petroleum-based, does not release toxins and is safe under average conditions of use.
Emerging Sustainable EPS Solutions
Scientists are also working actively on bio-EPS from vegetation-based materials and even biodegradable expanded polystyrene. While many of these alternatives are still going to be industrial composted or undergo special processing, they are welcome steps toward reducing expanded polystyrene’s impact on the environment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of EPS
The EXPANDED POLYSTYRENE (EPS) Market: Key Players and Trends
With extensive uses in construction, packaging, and industrial applications, Expanded polystyrene in construction continues to be one of the largest demand drivers.
Key Global Suppliers
Some major companies have their fingers in the worldwide EXPANDED POLYSTYRENE market:
- TotalEnergies (France): Supplies expanded polystyrene under its label, TotalE PS, with sustainability greatly stressed.
- Synthos (Poland): Concentrated on innovative, greener expanded polystyrene products.
- BASF SE (Germany): A leading chemical manufacturing house with best-performance expanded polystyrene material sales for thermal and packaging applications.
- Alpek (Mexico): Lead Americas expanded polystyrene supplier in various end-user markets.
- ACH Foam Technologies (USA): Renowned for the construction of insulation and geofoam products.
- SHOBEIR SHIMI (Middle East): A rising regional company renowned for offering Expanded polystyrene beads and molded-to-order products to various industries, with increasing export potential.
Key Regional Markets and Growth Drivers
- Asia-Pacific leads global expanded polystyrene consumption, fueled by rapid infrastructure development and packaging demands in China and India.
- Europe and North America focus more on Expanded polystyrene insulation and energy-efficient building systems, encouraged by stringent regulations around thermal performance.
- The Middle East and Africa are emerging markets where companies like Shabir Chemicals are expanding local supply chains to meet growing construction needs.
Market Trends and Sustainability Focus
Several trends are affecting the expanded polystyrene eps price and demand:
- Eco-Friendly Innovations: With growing concern for the environment, greater attention is being put on Expanded polystyrene recycling and developing biodegradable or circular EPS
- Improved Insulation Standards: Interest in energy-efficient buildings is driving interest in Expanded polystyrene eps r R-value, especially in extreme temperatures.
- Lightweight Construction Materials: Construction professionals are opting for expanded polystyrene because of its huge strength-to-weight ratio and reduced expanded polystyrene weight, thereby making transportation and on-site installation more cost-effectively feasible.
Because sustainability is becoming more of a theme, manufacturers and consumers alike are focusing on reducing wastage and seeking closed-loop reuse of EPS.
Conclusion
EXPANDED POLYSTYRENE is not just a packaging material—it’s a cost-effective, high-performance material for most industries. From protective light packaging to effective Expanded polystyrene insulation panels in green buildings, expanded polystyrene combines function with flexibility.
Its thermal insulating property, driven by positive Expanded polystyrene eps r value, makes it essential in energy saving in residential and commercial buildings. Also, its lightweight composition, varied uses, and controllable Expanded polystyrene properties make it invaluable across sectors. As recycling technology for expanded polystyrene improves and green suppliers become more available, expanded polystyrene’s future is with sustainability initiatives. Constant research and development maintain Polystyrene foam adaptable and forward-looking. As businesses pursue greener operations, expanded polystyrene will remain at the forefront—performance, cost, and environmental responsibility.
