A common and critical question regarding food packaging and storage materials is: “Is high density polyethylene food safe?” The definitive answer is yes—high density polyethylene (HDPE) is widely considered safe for food contact. This plastic is extensively used in various food applications, including containers for dairy products, juices, water, and numerous other consumables. In this article, we will thoroughly explore the safety profile of HDPE, addressing common inquiries such as “is high density polyethylene food safe for humans?”, “is HDPE 2 food safe?”, and reinforcing that HDPE plastic food safe standards are widely met. We will clarify why HDPE is food grade and emphasize its reliability for your everyday needs.
FDA Approval and Food Safety Standards
When discussing HDPE containers food grade reliability, the overwhelming consensus from regulatory bodies and scientific research is clear: HDPE is food safe. This robust plastic (often identifiable by the recycling code “2” – hence the relevance of “2 HDPE food safe”) is a cornerstone of the food packaging industry precisely because it poses no significant risk when in contact with edibles. The properties that make it durable and versatile also contribute to its safety for foodstuffs.
FDA Approval and Food Safety Standards for HDPE Plastic
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in ensuring that plastics used in food contact are safe. The FDA explicitly designates HDPE as a food-safe plastic. Specifically, virgin HDPE (material that has not been previously used or recycled) is approved for direct contact with food, making it a popular and trusted choice in the food packaging industry. This confirms that, unequivocally, virgin high density polyethylene is food safe. It’s a common choice for food-grade plastic because it’s durable, lightweight, easy to clean, and resistant to corrosion and mold. Furthermore, one of its most critical safety attributes is that it doesn’t leach harmful chemicals into food during normal use and can be safely reused for its intended purpose. This directly answers the question “is hdpe plastic safe for food” in the affirmative for virgin material.

However, it’s important to note that the FDA reviews recycled HDPE products on a case-by-case basis. This scrutiny is due to the potential for contamination during the recycling process, where previous contents of the plastic (if not food-related) or impurities introduced during collection and reprocessing could compromise its food safety. A material is FDA compliant if it meets all of the FDA’s guidelines for safe, direct contact with food, which includes strict purity standards for recycled content if it’s to be designated food grade.
Strength and Durability of HDPE Plastic Safe for Food Use
The inherent strength and durability of HDPE are significant factors contributing to its widespread adoption as a food-safe plastic. HDPE possesses strong intermolecular forces and high tensile strength due to its largely linear molecular structure with minimal branching. This structural integrity translates into exceptional robustness; for example, a mere 60-gram HDPE container can reliably hold over a gallon of liquid or approximately eight pounds of product. This impressive strength, combined with its resistance to impact and tearing, means that HDPE containers can protect food effectively from external contamination and damage, maintaining product quality and safety from manufacturing to consumer use. This reinforces why HDPE is food safe for rigorous packaging applications.
Is High Density Polyethylene Food Safe for Humans?
When considering specifically “is high density polyethylene food safe for humans?”, the answer remains a strong yes. It is essential to note that under normal conditions of use (as designed for its purpose), HDPE does not leach harmful chemicals into food. Extensive studies and regulatory oversight have consistently shown that HDPE is biologically inert when ingested and poses no significant health risks during its intended normal use. This property makes it exceptionally suitable for a vast array of food applications where human contact and consumption are direct.
However, while HDPE itself is safe, crucial caution should always be exercised with HDPE containers that previously held non-food items. For instance, former containers that stored chemicals, cleaning agents, or automotive fluids should never be repurposed for food storage due to potential residual contamination risks, even if the plastic itself is technically food-grade. Always ensure that any HDPE plastic used for food has been originally designated for food contact. This also applies to the broader question of “is polyethylene food safe?” – specific grades and proper handling are key
Is HDPE 2 Food Safe? Understanding Recycling Codes
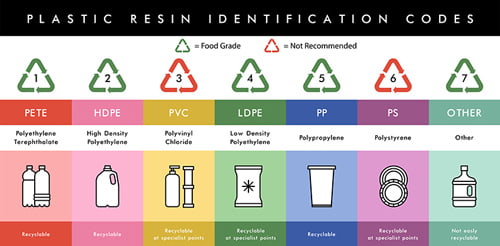
HDPE is commonly identified by the recycling code “2,” typically found inside a chasing arrows triangle symbol on the bottom of plastic containers. This designation (often referred to as “HDPE 2 plastic food safe”) explicitly indicates its composition as High-Density Polyethylene. This number directly confirms that products made from this type of plastic are generally considered safe for food contact, provided they are virgin material or specifically approved recycled HDPE. The FDA’s approval of HDPE as a food-contact substance directly reinforces the idea that “is HDPE 2 food safe?” – the answer is overwhelmingly yes, provided the material has not been contaminated with harmful substances during its lifecycle. Always look for the recycling code #2 when seeking HDPE containers food grade for peace of mind.

Clarifying: Is HDPE Food Grade?
To fully summarize the inquiry about whether HDPE plastic food safe, it’s important to understand the concept of “food grade.” A material is designated food grade when it meets all regulatory requirements (like those from the FDA) for safe contact with food. HDPE excels in meeting these standards. Both virgin HDPE and properly processed, FDA-approved recycled HDPE are recognized as safe for food applications.
The food-grade status of HDPE is attributed to several key properties:
- Non-Leaching: As mentioned, it does not transfer harmful chemicals into food.
- Durability: It can withstand repeated use and cleaning without degrading in a way that would release substances.
- Resistance to Chemical Reactions: It does not react with acidic, alkaline, or other food components, preserving the food’s quality and safety.
- Non-Absorbent: Its non-porous surface prevents food absorption, making it hygienic and easy to clean.
These combined attributes make HDPE an excellent choice for storing, transporting, and packaging a vast array of foods and beverages without compromising safety or quality. Therefore, when asking “is HDPE food grade?”, the answer is a resounding yes for properly manufactured virgin and certified recycled HDPE.
Concerns About PFAS in Fluorinated HDPE Containers Food Grade
While HDPE itself is generally considered safe for food contact, recent studies have highlighted a specific concern related to fluorinated HDPE containers. Fluorination is a process sometimes used to create a barrier layer on the inner surface of plastic containers to prevent the permeation of aggressive chemicals (like pesticides or solvents) stored within.
However, research has raised concerns about these fluorinated HDPE containers potentially leaching per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) into foods. These substances are often referred to as “forever chemicals” due to their extreme persistence in the environment and human body, and their association with various health concerns. Studies indicate that PFAS can migrate from such fluorinated HDPE containers into various foods or liquids stored within them, posing a risk of exposure to these harmful chemicals.
It is crucial to understand that this concern pertains specifically to HDPE containers that have undergone fluorination, typically used for non-food chemicals, and not to the vast majority of non-fluorinated HDPE plastic food safe products widely used for food packaging. Consumers should be aware of this distinction and ensure their HDPE food containers are explicitly certified as food grade and ideally, not sourced from industries where fluorination is common unless specifically stated as safe for food by the manufacturer.
Conclusion: HDPE Safe for Your Food Storage Needs
In conclusion, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is a highly reliable and extensively trusted material for food packaging and storage. Its widespread FDA approval, combined with its inherent properties such as durability, chemical inertness, and resistance to leaching, collectively ensure that HDPE plastic is safe for food and human consumption when used appropriately.
As consumers become increasingly aware of the materials used in their food containers, understanding the robust safety profile of HDPE (including the “2 HDPE food safe” designation) can empower them to make informed choices about their food storage options. While vigilance regarding fluorinated variants is prudent, the vast majority of HDPE products remain a testament to safe and effective plastic engineering in the food industry. You can confidently rely on properly designated HDPE containers food grade for your daily needs, knowing that HDPE is food safe.







درج دیدگاه