Polyethylene (PE) is a thermoplastic polymer that stands as one of the most fundamental and widely utilized materials in the global manufacturing landscape. As a core component of the polyethylene plastics family, this versatile PE material is indispensable across countless sectors, from advanced industrial packaging to critical infrastructure. Its adaptability stems from a unique combination of polyethylene material properties, including exceptional chemical resistance, durability, and processing flexibility. Accounting for over a third of the world’s total plastics production, its economic and industrial significance cannot be overstated.
For international traders, suppliers, and industrial buyers, a deep understanding of the properties of polyethylene is essential for sourcing the right material for specific applications. Navigating the complexities of molecular weight, density, and melt flow index is critical to ensuring performance, quality, and cost-effectiveness. This guide provides an authoritative overview of the polyethylene structure, its primary classifications, manufacturing processes, and key polyethylene industrial applications, offering the crucial information needed to make informed procurement decisions in a competitive global market.

Understanding Polyethylene: Chemical Composition and Structure
At its core, what is polyethylene material? It is a synthetic polymer created through the polymerization of its basic building block, the polyethylene monomer ethylene (C₂H₄), a gaseous hydrocarbon derived primarily from natural gas or petroleum. During a process known as addition polymerization, the double bond in each ethylene monomer breaks, allowing them to link together to form long, saturated, and highly stable hydrocarbon chains with remarkable consistency.
The fundamental polyethylene formula is represented as (-CH₂-CH₂-)n, signifying its repeating ethylene units. This simple, linear polyethylene chemical structure is the foundation for its diverse properties. The ‘n’ in the formula represents the degree of polymerization—the number of monomer units in the polymer chain—which can range from hundreds to thousands, directly influencing the material’s molecular weight.
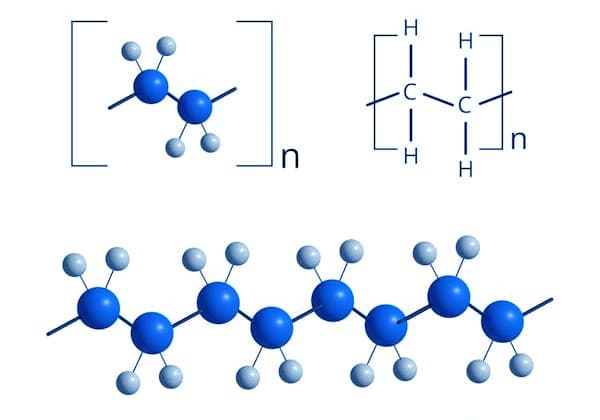
Key structural characteristics that define a specific grade of polyethylene include:
- Molecular Weight (MW): The average length of the polymer chains. Higher MW generally results in enhanced toughness, impact strength, and environmental stress crack resistance (ESCR), but can make the material more difficult to process.
- Molecular Weight Distribution (MWD): The range of chain lengths within a given resin. A narrow MWD (where chains are of similar length) often yields better clarity and less warpage, while a broad MWD can improve processability and resistance to stress cracking.
- Chain Branching: The degree of which shorter polymer chains branch off from the main backbone. The level of branching is the primary factor that determines the material’s density and crystallinity. As a thermoplastic, PE plastic can be melted and reformed upon cooling, allowing it to be easily processed into a vast array of polyethylene products through methods like extrusion, injection molding, and blow molding.
Polyethylene Properties: Physical and Chemical Characteristics
The performance of any polyethylene product is dictated by its inherent properties, which vary significantly between different grades.
Polyethylene Physical Properties
- Density and Crystallinity: Density is a primary determinant of a grade’s performance and is directly related to the degree of crystallinity. More linear polymer chains (less branching) can pack together more tightly, leading to higher crystallinity and thus higher density (e.g., HDPE). Highly branched chains create more space between them, resulting in lower crystallinity and lower density (e.g., LDPE). Higher density generally correlates with greater strength, rigidity, hardness, and heat resistance. Density ranges from approximately 0.910 g/cm³ for LDPE to 0.965 g/cm³ for HDPE.
- Melting Point: The melting temperature for polyethylene (PE) is determined by its crystalline structure, ranging from 105°C to 135°C. More crystalline types like HDPE have a higher, more defined melting point, whereas LDPE has a lower, broader melting range.
- Tensile Strength and Modulus: High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) exhibits excellent tensile strength and a high flexural modulus, making it suitable for applications requiring structural integrity, such as pressure pipes and industrial containers.
- Flexibility and Toughness: Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) and Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) are known for their high flexibility and exceptional impact resistance, even at low temperatures, making them ideal for film and packaging applications where durability is paramount.
- Optical Properties: The structure of polyethylene influences its clarity. The smaller, more disordered crystalline structures in LDPE and LLDPE allow light to pass through, offering good transparency for film applications. Conversely, the larger, more organized crystalline structures in HDPE scatter light, making the material naturally opaque.
Chemical Properties of Polyethylene
- Chemical Resistance: One of the most valued properties of polythene is its exceptional resistance to a wide range of chemicals. It is highly resistant to water, most acids, bases, alcohols, and esters. This makes it a first-choice material for chemical storage tanks, laboratory ware, and transport containers. However, it can be attacked by strong oxidizing agents and certain chlorinated or aromatic hydrocarbons.
- Environmental Stress Crack Resistance (ESCR): ESCR is the ability of a material to resist failure when exposed to a combination of mechanical stress and an attacking chemical agent (like a soap or detergent). This is a critical property for products like detergent bottles, pipes, and fuel tanks. HDPE grades, particularly those with a broad MWD, offer excellent ESCR.
- Moisture Resistance: PE plastic material has very low water absorption, providing an excellent moisture barrier for food packaging, pharmaceutical containers, and construction applications.
- Electrical Insulation: Polyethylene is an outstanding electrical insulator with a high dielectric strength and low dielectric constant, leading to its widespread use for primary insulation of wires and cables in both power and telecommunications.
Polyethylene Grades and Classification
Polyethylene grades are categorized based on their density, branching, and crystallinity, providing unparalleled characteristics for various applications.
The Polyethylene Manufacturing Process
Polyethylene production is achieved through the addition polymerization of ethylene gas in large-scale industrial reactors. The specific polyethylene manufacturing method, catalyst, and reactor conditions (temperature, pressure) determine the final grade.
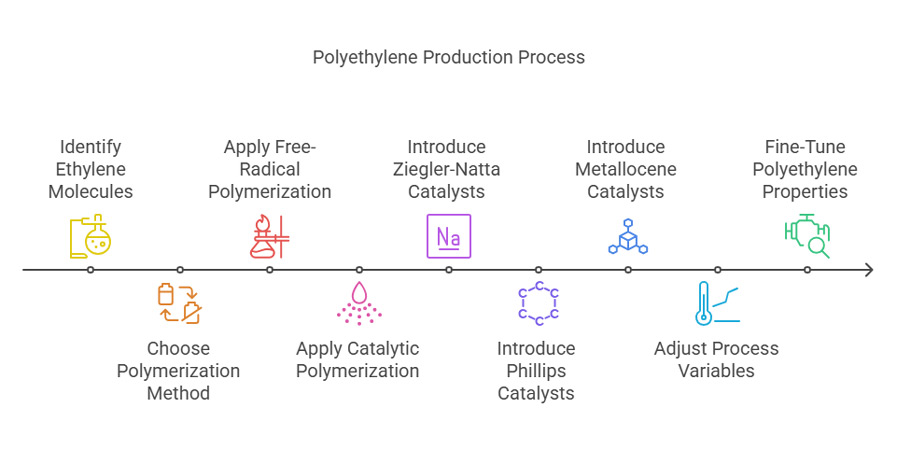
- Polymerization Methods: The answer to what type of polymerization does polyethylene undergo depends on the desired grade. High-pressure free-radical polymerization (up to 3,000 bar) is used to produce LDPE, resulting in a randomly branched molecular structure. Catalytic polymerization, operating at much lower temperatures and pressures, is used for HDPE and LLDPE, creating more linear, crystalline structures with controlled branching.
- Reactor Technologies:
- Slurry Process: Used for HDPE, this process involves polymerizing ethylene in a liquid hydrocarbon diluent, where the resulting PE forms as solid particles.
- Gas-Phase Process: The most common method for both HDPE and LLDPE, where gaseous ethylene is polymerized over a fluidized bed of catalyst.
- Solution Process: Used for certain specialty grades, ethylene is dissolved in a solvent at high temperatures, and polymerization occurs in the liquid phase.
- Key Catalysts: The development of advanced catalysts was a revolution in PE polymer production.
- Ziegler-Natta Catalysts: Enable the production of HDPE and LLDPE with controlled structures, typically resulting in a broad MWD.
- Phillips Catalysts: Chromium-based catalysts primarily used for manufacturing HDPE, known for producing resins with excellent stiffness and ESCR.
- Metallocene Catalysts: A newer class of single-site catalysts that allow for precise control over the polymer structure and co-monomer incorporation, yielding materials with a narrow MWD and enhanced properties like strength and clarity.

Key Polyethylene Uses and Industrial Applications
Given its versatility, polyethylene is one of the most widely used plastics in modern industries. What is polyethylene used for? From simple plastic bags to high-performance industrial components, polyethylene finds applications across various fields due to its durability, chemical resistance, and lightweight nature.
1. Packaging Industry
The dominant use for polyethylene is in packaging. PE poly bag films made from LDPE and LLDPE are used for everything from food packaging and shrink wrap to industrial liners and heavy-duty sacks. In rigid packaging, bottles and containers made from blow-molded HDPE are standard for milk, juice, detergents, and industrial chemicals due to their excellent chemical resistance and strength.


2. Construction and Infrastructure
Polyethylene plays a crucial role in construction due to its resistance to moisture, chemicals, and impact. PE Pipes and HDPE pipes are commonly used for water and gas distribution, ensuring durability and leak resistance. Insulation materials made from polyethylene help maintain energy efficiency, while geomembranes provide essential barriers for landfill and construction projects.
3. Medical and Healthcare
In the medical industry, polyethylene is valued for its sterility and biocompatibility. Medical tubing and surgical trays ensure safe fluid transport and storage. Prosthetics and orthopedic implants, particularly those made from Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), offer durability and compatibility with the human body. Additionally, sterile packaging for pharmaceuticals helps protect medicines from contamination.


4. Consumer Goods
Polyethylene is widely used in everyday household items such as storage containers, kitchenware, and toys. PE Fabric is a common material in waterproof clothing, making it ideal for raincoats and outdoor gear. Its lightweight and flexible nature make it suitable for recreational equipment and durable home products.
5. Automotive and Transportation
The automotive industry benefits from polyethylene’s lightweight and fuel-efficient properties. It is used in fuel tanks, vehicle interiors, and protective linings. By reducing vehicle weight, polyethylene helps improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, making it an environmentally friendly choice.

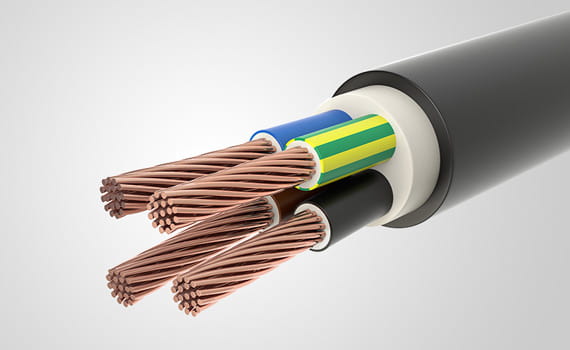
6. Electronics and Electrical Applications
Polyethylene serves as an excellent insulator for wires and cables, preventing electrical hazards. Protective casings for electronic devices enhance safety, while semiconductor packaging ensures the longevity of electronic components.
7. Agriculture and Environmental Applications
Farmers rely on polyethylene for greenhouse films, mulching sheets, and irrigation solutions. PE Tubing is widely used in drip irrigation systems, ensuring efficient water distribution. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop biodegradable and recyclable alternatives to minimize environmental impact.


8. Specialized and High-Performance Uses
Polyethylene is found in high-tech applications, including bulletproof vests made from UHMWPE fibers, aerospace components, and 3D printing filaments. These specialized uses demonstrate its strength, adaptability, and potential for innovation.
Supply, Packaging, and Global Trade
At Shobeir Shimi, we are a leading provider of polyethylene material solutions, ensuring our products meet stringent international standards for quality and logistics to facilitate a reliable global supply chain.
- Packaging: Our polyethylene grades are typically supplied in 25 kg bags, palletized and shrink-wrapped for security and ease of handling. For large-volume orders, we offer 1,000 kg or 1,250 kg jumbo bags (super sacks) to optimize handling, reduce packaging waste, and streamline loading into production silos.
- Logistics and Export: We manage containerized shipments globally, with standard loading capacities of 18-26 metric tons per 20-foot or 40-foot container, depending on the product form and packaging. All shipments are accompanied by comprehensive documentation, including a Certificate of Analysis (COA) detailing the specific properties of the batch, to ensure quality consistency and seamless customs clearance. We are proficient in all major shipping incoterms (FOB, CIF, etc.) to meet diverse client procurement strategies.
Environmental Profile and Polyethylene Recycling
While highly durable, the environmental impact of polythene polyethylene is a critical consideration in a world moving towards a circular economy. Polyethylene is a highly recyclable material, with HDPE (recycling code #2) and LDPE/LLDPE (recycling code #4) being widely reprocessed through mechanical recycling. This process involves collecting, sorting, shredding, washing, melting, and re-pelletizing the material. Recycled PE is used to manufacture non-food bottles, plastic lumber, pipes, composite materials, and bags.

The industry continues to innovate with bio-based polyethylene (derived from renewable resources like sugarcane) and advanced (chemical) recycling technologies like pyrolysis, which can convert mixed plastic waste back into a valuable feedstock for producing new polymers. These efforts are crucial for reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing plastic waste.
Conclusion
From its simple polyethylene composition to its vast range of applications of polyethylene, this material has proven to be one of the most important innovations in modern science. Its unparalleled combination of strength, chemical resistance, low cost, and processability ensures it will remain a critical resource for industries worldwide. For any manufacturer, understanding the nuances between the different polyethylene types and their specific properties is the key to optimizing product performance, ensuring quality, and unlocking its full potential for any application.
For technical data sheets, price inquiries, or to discuss your specific material requirements, contact our team of polymer specialists today.

