ACRYLONITRILE BUTADIENE STYRENE (ABS) is classified as a thermoplastic polymer and is an important material in multiple sectors. This robust and versatile plastic stems from the copolymerization of three monomers, which are acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. Each monomer brings building block attributes that expand the domain of functionality offered by this ABS plastic. The automotive and consumer electronics industries are two examples of industries that use ABS due to its strength, toughness, flexibility, and heat resistance. In addition to these industries, others include construction, electronics, and consumer goods; all of which ABS offers durability and performance at a cost-effective price.
Due to the reliable combination of Acrylonitrile butadiene Styrene properties at an affordable price, it has gained popularity over the last couple of years. While relying on high-performance materials aimed at improving efficiency, ABS remains a primary choice for designers and producers across the globe. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene abs polymer has become particularly significant in industries that require materials that endure physical impact, elevated temperature, or chemicals while maintaining performance.
ABS GRADE LIST
| GRADE | PRODUCER | MFR | DENSITY | DATASHEET |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F232 | JAM | 14 | 1.04 | download |
| F332 | JAM | 14 | 1.04 | download |
| P30 | JAM | — | 1.04 | download |
| T161B | JAM | — | 1.04 | download |
| L322 | JAM | 23 | 1.04 | download |
| T6306 | JAM | — | 1.04 | download |
| B432 | JAM | 4 | 1.04 | download |
| T6 302 | JAM | — | 1.04 | download |
| B183 | JAM | — | 1.04 | download |
| BR 245 | JAM | — | 1.04 | download |
| B532/E | JAM | 5 | 1.04 | download |
| C442 | JAM | 6 | 1.04 | download |
| BR 277 | JAM | — | 1.04 | download |
| B732/E | JAM | 4.5 | 1.04 | download |
| E332 | JAM | 10 | 1.04 | download |
| SD0150 | TABRIZ | 1.8 | 600 | download |
| D232/M3 | JAM | 8 | 0.04 | download |
What is Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is a thermoplastic made from a blend of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene.
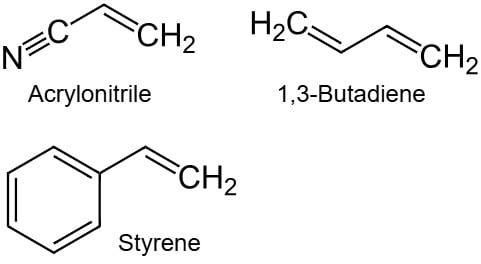
Each monomer adds different Acrylonitrile butadiene Styrene properties to the final polymer:
- Acrylonitrile imparts chemical and thermal stability to ABS. It does not degrade from exposure to a variety of aggressive chemicals and high temperatures.
- Impact strength and toughness are the roles played by butadiene, enabling Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene Structure to be shock-absorbing without cracking or breaking, of immense benefit for products subjected to rough handling.
- Styrene adds gloss and aids the material’s processability, which makes ABS easier to mold into complex geometries with a glossy finish.
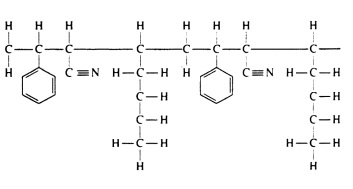
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene production
There are two primary methods of producing Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene: the emulsion process and the continuous mass process.
In the emulsion process, the three monomers are polymerized in a water-based solution with surfactants to create smaller, finely divided particles of ABS. This process is generally less expensive and easier to scale for mass production.
The bulk polymerization process of the monomers to create larger, more uniform particles of ABS for extrusion or injection molding is what the steady-state mass process involves. The method of production can affect the molecular weight, mechanical properties, and processing behavior of the final ABS product.
Key Properties of ABS
ACRYLONITRILE BUTADIENE STYRENE (ABS) is known to have equally well-rounded properties, and hence it is appropriate for many applications. Its chemical, thermal, as well as mechanical Acrylonitrile butadiene Styrene properties are among the key reasons it has been discovered in widespread application.
| Property | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.03 | kg/m³ |
| Elastic modulus | 2000 | MPa |
| Poisson’s coefficient | 0.394 | |
| Yield stress | 45-60 | MPa |
| Specific heat | 1386 | J/(kg K) |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.2256 | W/(m K) |
Mechanical Properties
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is highly impact-resistant, i.e., it can absorb and disperse energy during sudden loading and hence is an excellent material to be used where endurance and physical stress resistance are needed. It also has toughness and rigidity, i.e., it doesn’t deform under stress and still maintains shape and structural strength. Because of these characteristics, ABS becomes an essential component of motor vehicle parts, household appliances, and consumer electronics.
Chemical and Thermal Stability
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is resistant to many chemicals, such as acids, alkalis, and oils, because of which it is applied in those applications that require exposure to harsh environments, for instance, industrial or automotive machinery. The Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene abs polymer is also thermally stable, capable of resisting deformation or weakening upon exposure to elevated temperatures, which is important in Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene uses like electrical enclosures, automotive dashboarding, and even some medical devices.
Limitations
Despite its many advantages, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene has some limitations. One of the notable limitations is that it possesses poor solvent resistance; ABS swells, cracks, or degrades in exposure to certain solvents, such as acetone or ketones. It is, hence not ideal for use in certain chemical environments unless some protective measures are employed. It is also prone to UV degradation, i.e., it becomes brittle and color-fades when subjected to direct sunlight. Hence, ABS products destined for external applications usually need UV stabilizers or protective coatings.
Applications of ABS across Industries
As a result of its mechanical durability, thermal stability, and ability to be processed easily, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is essential across different fields. Below are some of the principal sectors where ABS is highly utilized:
- Automotive Parts
In the automotive field, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is used widely in the production of components such as dashboards, bumpers, and interior trims. The provided impact resistance of ABS is very important for these applications, which require the part to withstand physical stress, minor bumps, and changes in temperature without deformation or cracking. Further, molding ability enables ABS to be shaped into complex parts with intricate aesthetic and functional features.

- Consumer Goods
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is currently the favorite material that is used to produce various consumer household products, such as toys, appliances, and kitchenware. The best example of a product utilizing such a product with ABS is LEGO bricks, which are made using ABS due to its great strength, high precision, and high wear resistance. It is also utilized in household items such as vacuum cleaners, food processors, and hairdryers.

- Construction
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is used in construction for fittings and pipes. Its high resistance to chemicals makes it an ideal material for plumbing systems, especially in chemical transportation or hot water applications. Its pipes are simple to install and are long-lasting, even in extreme conditions.
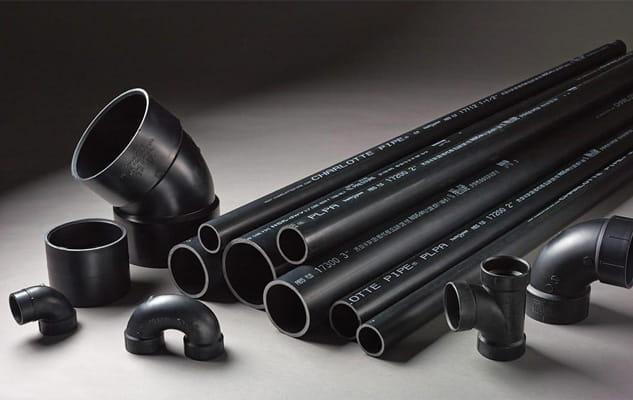

- Electronics
The insulating features of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene protected sensitive electronics from electrical engineering and enabled the strength and rigidity of electronic components to be secured. As a result, it is widely utilized for housing and keyboards of various electronics. It is also used in the production of computer peripheral devices, phone cases, TV enclosures, and the external casing of the computers, where both durability and aesthetic features are needed.

- 3D Printing and Rapid Prototyping
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene has carved out a key role in 3D printing and rapid prototyping. Its impressive strength, durability, cost-effectiveness, and straightforward processing and finishing qualities make it a go-to material for crafting functional prototypes, detailed models, and small-batch production components. ABS shines particularly in Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) or Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printers, where its reliability stands out.

- Medical Devices and Equipment
The medical industry is blessed with Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene because it can withstand long periods, can be sterilized, and devices like compressors, nebulizers, and medical tools. It may be molded to precise shapes, is tough, and extremely chemical breakdown-resistant, thus making it a perfect candidate for medical usage that requires durability and consistency of performance.
In short, ABS is everywhere.
Top Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene Supplier
SABIC and Shobeir Shimi stand out as the primary and secondary suppliers of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene. These firms are known to supply very qualitative ABS resin for different industries. SABIC, the world’s leading company in petrochemicals, is also one of the most innovative companies in terms of ABS production. The company offers multiple grades of ABS for various applications. Shobeir Shimi is also a leading supplier from the region who offers competitive ABS products that meets the needs of the processors in the region. Both suppliers are crucial to the global supply of ABS as they make sure processors are provided with quality materials to sustain their production.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ABS
Advantages of ABS
- Versatility: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is extremely simple to shape into many forms with methods like injection molding, extrusion, and thermoforming. This makes it highly versatile for the production of complex parts for so many different industries, ranging from automobiles to electronics.
- Recyclability: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is recyclable, and this makes the production process minimize waste and be more sustainable. Recycling ABS reduces environmental impact by limiting the use of raw materials.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is generally less expensive than other engineering ABS plastics, and therefore, it is utilized extensively by manufacturers who desire performance and cost of production.
Disadvantages of ABS
- Poor Weathering: One of the biggest drawbacks of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is that it suffers from UV degradation. It tends to become brittle, lose color, and degrade in strength if exposed to sunlight for a prolonged duration of time. Therefore, ABS is generally used in indoor applications or requires additional UV stabilizers for outdoor applications.
- Solvent Sensitivity: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is sensitive to certain chemicals, especially solvents like acetone, which can swell or degrade it. This makes it unsuitable for use in environments where it may be directly exposed to harsh solvents without additional chemical protection.
ABS vs. Other Thermoplastics
Comparing ABS to other popular thermoplastics such as PLA, PVC, and polycarbonate, the following major differences are realized:
- ABS vs. PLA: PLA, or polylactic acid, is an eco-friendly and biodegradable plastic derived from renewable resources. While PLA is less impact-resistant and tough than ABS, it is not suitably designed to be utilized in applications that require strength and rigidity.
- ABS vs. PVC: PVC is a rigid and chemically resistant material, but ABS beats PVC when impact strength and moldability are needed. ABS works better in flexible applications like auto parts or enclosures for electronic devices.
- ABS vs. Polycarbonate: Polycarbonate is stronger and more heat-resistant than ABS, but is typically more expensive. ABS is typically selected since it is less expensive, especially where heavy heat resistance is not the primary consideration.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene can be used where there is a need for strength, toughness, and processability. It is particularly useful where cost, impact strength, and durability are key considerations.
Sustainability and Recycling in ABS Production
With the increase in demand for renewable materials, there is a concurrent increase in interest in the bio-based production and the recycling of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene materials:
- Bio-Based ABS: Manufacturers are looking into the possibility of utilizing bio-based feedstocks, such as those derived or sourced from plant material, to produce bio-based and petroleum-based ABS. This shift could potentially lessen the reliance on petroleum and also help in lowering the carbon footprint associated with ABS production. Even though bio-based ABS is not fully realized and developed yet, its existence is towards more sustainable practices.
- Recycling: Recycled Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is continuously used in numerous industries which in turn makes ABS materials easy to recycle. Coupled with the need to reduce waste, recycled ABS supports the circular economy and is commonly found in vehicle parts, consumer products, and construction materials.
- Environmental Impact and Regulations: The public and regulatory bodies expect the continual reduction of the environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene toxicity, which puts pressure on manufacturers. As a result, most ABS manufacturers are investing in cleaner methods of production and putting resources towards new materials that serve their purpose yet are environmentally friendly.
Conclusion
From automotive, electronics, medical, and consumer goods, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is a highly useful and valuable material that is employed in a wide variety of industries. It is one of the most popular materials in manufacturing due to its impact resistance and stability to chemicals and its ease of processing. Although it does have limitations, such as poor sensitivity to weathering and solvents, the advantages of being cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and easily recyclable continue to make it immensely popular. In the case that you’re searching for a trustworthy supplier for your next project, looking into Shobeir Shimi and SABIC will provide you with quality materials. Also, keeping an eye on new developments in bio-based and recycled ABS will help you incorporate more eco-friendly options into your manufacturing processes.
