LDPE is a type of polyethylene characterized by its branched molecular structure, which gives it unique properties compared to other polyethylene types. When combined with various additives through a process called compounding, LDPE becomes even more versatile, allowing manufacturers to tailor its properties for specific applications. From packaging materials to agricultural films and construction products, LDPE compound is crucial in enhancing product quality and performance across diverse sectors.
Need assistance choosing the ideal LDPE compound for packaging films, agricultural mulch, or medical tubing? Contact our specialists today to customize your formulation with additives like UV stabilizers, antioxidants, or flame retardants, ensuring flexibility, durability, and top performance for your application.

Compound Additives
LDPE compound includes additional substances mixed with the base LDPE:
- Stabilizers: To protect against degradation from heat, light, or oxidation.
- Antioxidants: To prevent oxidation during processing and use.
- Colorants: To add color to the final product.
- Processing Aids: To improve manufacturing processes.
- Fillers: To modify properties or reduce costs.
Examples of LDPE Compounds
- Transparent, flexible tubing: might have an anti-oxidant for extended use.
- Black, flame-retardant plastic bin: would likely contain a flame retardant and a colorant.


Benefits of LDPE Compounds
Advantages of LDPE Substances:
-
Tailored Properties
By adding particular modifiers, manufacturers can produce LDPE compounds that are perfect for a range of applications.
-
Enhanced Performance
Additives can enhance LDPE’s strength, resilience to weather, and other qualities.
-
More significant Usage
LDPE compounds can be applied in scenarios where LDPE as itself wouldn’t be appropriate.
LDPE Compounds Applications
LDPE compounds find extensive use across various industries due to their unique combination of properties:
- Packaging Industry: Used in film applications such as shopping bags, food packaging, and shrink wrap due to its flexibility and transparency.
- Agriculture: Employed in greenhouse films, mulch films, and irrigation pipes because of its durability and resistance to environmental conditions.
- Medical Devices: Utilized in manufacturing flexible containers, tubing, and closures for pharmaceutical products due to their chemical resistance and clarity.
- Electronics: Applied in wire and cable insulation and as a protective layer for electronic goods due to its excellent electrical properties.
LDPE Compounds Processing
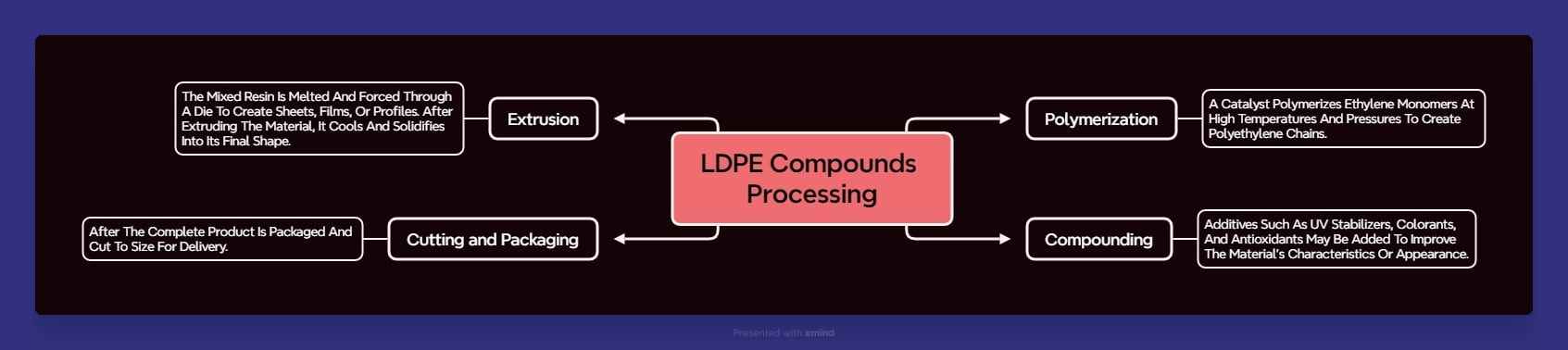
There are multiple essential phases in the manufacture of LDPE compounds:
1. Polymerization:
A catalyst polymerizes ethylene monomers at high temperatures and pressures to create polyethylene chains.
2. Compounding:
Additives such as UV stabilizers, colorants, and antioxidants may be added to improve the material’s characteristics or appearance.
3. Extrusion:
The mixed resin is melted and forced through a die to create sheets, films, or profiles. After extruding the material, it cools and solidifies into its final shape.
4. Cutting and Packaging:
After the complete product is packaged and cut to size for delivery.
Conclusion
The polymer that makes up LDPE is a chain of ethylene units that repeat and have branches that affect its characteristics. Manufacturers can add different chemicals to LDPE to generate compounds with desired properties. These additions include UV stabilizers for sun protection, colorants for pigments, antioxidants for longer shelf lives, flame retardants for fire safety, and anti-static agents to lessen static electricity.
