What is polyethylene glue? What glue is best for polyethylene bonding? Polyethylene is famously difficult to glue. If you’ve ever tried to bond this type of plastic, you know it refuses to stick with standard adhesives. That’s because polyethylene has a low surface energy and a “waxy” feel, which repels conventional glues.
This comprehensive guide will solve that problem for you with polyethylene glue. We’ll cover all working methods—from industrial adhesives and hdpe glue to DIY tricks. You’ll learn exactly what glue works on polyethylene, including how to glue hdpe, step-by-step.
What Is Polyethylene? (And Why Won’t Standard Glue Stick?)
Polyethylene is a type of Low Surface Energy (LSE) plastic. Imagine trying to glue something with a waxy or oily surface—that’s what you’re dealing with in bonding polyethylene. The low surface energy means adhesives simply can’t wet the surface properly, causing most glue attempts to fail. What sticks to polyethylene? There are three main types of polyethylene, and each affects which polyethylene plastic glue works best:
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): Rigid and Strong
HDPE (high density polyethylene glue) is a tough, rigid plastic found in bottles, pipes, and cutting boards. When people ask how to glue HDPE, this is usually the material they mean. Hdpe adhesive is strong but tricky to bond without the right method.
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene): Soft and Flexible
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) is softer and more flexible. You’ll find it in plastic bags, tubing, and “squeezy” bottles. Its flexibility requires adhesives such ldpe glue and glue for polyethylene plastic that can stretch and hold without cracking.
PE Foam (Polyethylene Foam): Spongy and Light
Polyethylene foam is lightweight and spongy. It is commonly used in packaging, insulation, and crafts. What is the best adhesive for polyethylene foam? It needs specialized adhesives like polyethylene foam glue that remain flexible and won’t degrade the foam.
The 3 Proven Methods for Polyethylene Bonding
Standard glues usually fail on polyethylene bonding, but three methods consistently succeed for gluing polyethylene:
- Surface Treatment – Changing the surface to make it stickable.
- Specialized Adhesives – Using polyethylene adhesives formulated specifically for polyethylene.
- Specific Hot Melt – Dedicated hot melt sticks designed for polyethylene foam and similar materials.
This “3 S’s” framework is your roadmap to effective polyethylene bonding that we explain in the following.

Method 1: Surface Treatment (The “Secret” to What Sticks to Polyethylene)
How to glue polyethylene plastic? Surface treatment is the critical first step in polyethylene bond—most guides miss this. You must modify the surface energy for adhesives to bond.
- 1
Step 1: Cleaning and Abrading
Start by cleaning the surface thoroughly with isopropyl alcohol to remove oils and dust. Then, lightly scuff the area with sandpaper so the glue has a “key” to grip onto. A smooth, glossy surface won’t hold adhesive well.
- 2
Step 2: Chemical Primers (The Best DIY Option)
What glue sticks to polyethylene? Chemical primers are the best secret weapon for DIYers. Products like Loctite 770 chemically etch the surface, raising its surface energy. This pretreatment allows super glues and other polyethylene adhesive glue to stick firmly.
- 3
Step 3: Flame, Corona, or Plasma Treatment (The Industrial Method)
Industrially, flame, corona, or plasma treatments change the molecular structure of polyethylene surfaces. Industrial polyethylene adhesive is not practical at home but essential for factory-grade bonding. These methods prepare the surface perfectly for adhesives on a large scale.
Method 2: The Best Adhesives for Polyethylene (After Surface Prep)
After proper surface preparation, choosing the best glue for polyethylene is crucial. Here’s a buyer’s guide comparing the best options & adhesive for polyethylene:
- 1
Cyanoacrylates (Super Glue) + Primer
Super glue alone won’t work on polyethylene. But combined with a primer, it forms a quick and strong bond—ideal for small repairs and rapid fixes. Buy our Polyethylene Primer + CA Glue Kit here.
- 2
Structural Acrylics & Polyethylene Epoxy
For heavy-duty bonding, structural acrylics or specialized polyethylene epoxy are the go-to. These two-part systems (epoxy for polyethylen) are made specifically for LSE plastics, offering the strongest and most durable bonds and adhesives for polyethylene. Shop our industrial strength glue for plastic.
- 3
UV-Curing Adhesives
How to glue acrylic? UV-Curing adhesives is a newer option perfect for clear parts or controlled curing. These polyethelene glue cure when exposed to UV light, allowing precise application control and strong bonds on polyethylene surfaces.
Method 3: Gluing Polyethylene Foam & Using Hot Melt
How to glue polyethylene foam? For polyethylene foam, the glue for polyethylene foam is best for different materials. Pe foam differs due to the material’s softness.
- 1
Best Adhesive for Polyethylene Foam
Flexible adhesives like certain hot melts and contact cements provide the best results on PE foam. This polyethylene foams adhesive maintains flexibility and holds bonding polyethylene foam without damaging the material.
- 2
Using “PE” Hot Melt Sticks
Standard craft glue sticks are usually EVA-based and won’t stick well. You need polyamide or metallocene hot melt sticks designed specifically for polyethylene plastics. These provide a reliable and flexible bond. Buy our PE-compatible hot melt sticks.
Types of Adhesives Suitable for Polyethylene
When it comes to bonding polyethylene, various types of adhesives can be effective, each with unique properties suited for specific applications. Choosing the right polyethylene adhesive is crucial for achieving a strong and durable bond.
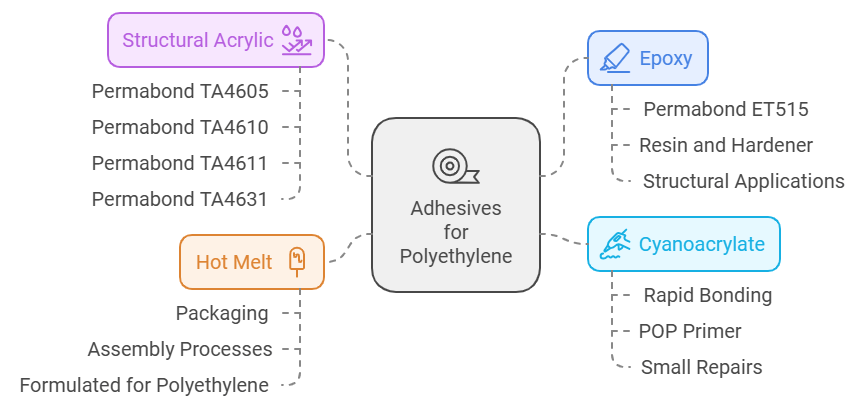
One of the most popular choices is epoxy adhesive. Epoxies are known for their strength and versatility, offering excellent adhesion to polyethylene when properly applied. Specific examples like Permabond ET515 provide a flexible epoxy solution that is particularly suitable for polyethylene applications. These adhesives typically consist of a resin and a hardener that, when mixed, chemically react to form a tough, durable bond. Epoxies can be ideal for structural applications, providing a strong hold under various environmental conditions for polyethylene bonding.
Cyanoacrylate (super glue) offers another bonding option. This fast-acting adhesive forms a bond by reacting with moisture in the air, making it suitable for small, quick repairs on polyethylene. While cyanoacrylate offers rapid bonding capabilities, it may not be as durable under stress or extreme conditions as epoxy. Companies like Permabond offer specialized primers, such as the POP Primer, which can enhance cyanoacrylate adhesion to polyethylene, improving its performance as a polyethylene plastic glue.
Hot melt adhesives are also commonly used for polyethylene applications. These adhesives are applied in a molten state and solidify upon cooling, creating a bond as they harden. They can provide a strong bond for various applications, especially in packaging and assembly processes. However, it is vital to select a hot melt adhesive specifically formulated for polyethylene.
A noteworthy recent development is the introduction of structural acrylic adhesives specifically designed for polyethylene. Permabond has developed a line of specialty adhesives, including TA4605, TA4610, TA4611, and TA4631. These adhesives bond low surface energy plastics and offer good impact and environmental resistance, making them an excellent option for rugged applications where a reliable polyethylene adhesive is needed.
For specific polyethylene repair and construction projects, products like TAP Poly Weld provide targeted solutions. This two-part epoxy adhesive requires flame treating the polyethylene surface to create a strong bond, making the polyethylene molecules more receptive to the polyethylene glue. This method is often employed when considering how to glue HDPE effectively.

Answering Your Questions: Polyethylene Glue Myth-Busters
Will polyethylene glue work? What glue works on hdpe? Can polyethylene be glued? Let’s address directly some common myths and FAQs from forum threads in this section:
Will PVC Glue Work on Polyethylene?
No. PVC cement is a solvent weld that melts and fuses PVC but does not adhere to polyethylene surfaces. This polyethylene pipe glue does not react with PE.
Will Epoxy Stick to Polyethylene?
No, standard 5-minute epoxy will not stick to polyethylene; they peel off easily. Only specialized polyethylene epoxies or structural acrylics designed for LSE plastics work.
Can You Glue Polyethylene Without a Primer?
No, we can’t glue polyethylene without a primer. Only specialized (and expensive) structural acrylics or by using hot melt adhesives can bond without primer. For most repairs (99% of repairs), a primer is the easiest, cheapest, and most reliable method.
How to Glue HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): A 5-Step Guide
How to glue hdpe together? Follow these steps for gluing hdpe to get a strong HDPE bond:
Step 1: Gather Your Materials
In the first step, you’ll need HDPE parts, sandpaper, isopropyl alcohol, PE primer, and your adhesive (e.g., CA glue).
Step 2: Clean and Abrade the Surface
Thoroughly clean the bonding area and roughen it with sandpaper.
Step 3: Apply the Polyethylene Primer
Coat the surface with a polyethylene primer like Loctite 770 to prepare the plastic.
Step 4: Apply the Polyethylene Adhesive
Apply your chosen polyethylene glue promptly to the primed surface.
Step 5: Clamp, Cure, and Test
Secure the parts and allow the polyethylene glue to cure fully before testing the bond.
Alternative to Gluing: Polyethylene Bonding with Welding
For large or critical repair hdpe plastic, gluing with polyethylene glue isn’t always the best option. Welding HDPE plastics is a professional method used for tanks, pipes, and structural repairs. Hot-air welding melts the plastic surfaces and fuses them, while friction welding uses mechanical heat to join parts without adhesives. For more detailed polyethylene bonding welding instructions, visiting an authoritative plastics industry website such as plastics industry association is recommended.
Find the Right Polyethylene Glue for Your Project
Now that you know how to glue polyethylene and what works best for HDPE, LDPE, and PE foam, it’s time to get the right adhesive. Whether you need a polyethylene adhesive for industrial use or a household fix, we offer the full range.
Since prices are subject to change at any time due to severe exchange rate fluctuations and rapid market changes, please contact on WhatsApp with us for polyethylene glue price inquiries.
You can also contact our sales experts for free consultation, comprehensive information about industrial polyethylene adhesive price list and buy of polyethylene glue, +polyethylene +adhesives.
Conclusion
Understanding both the material properties and the polyethylene glue options is essential for anyone needing to glue HDPE, LDPE, or PE foam effectively. Gluing polyethylene successfully requires recognizing and overcoming the unique challenges posed by its low surface energy and “waxy” surface, which make standard adhesives ineffective. The key to a strong, durable bond lies in proper surface preparation—cleaning, abrading, and preferably using a chemical primer to raise the surface energy. Without these steps, even the best adhesives struggle to stick. After surface treatment, selecting specialized adhesives such as polyethylene-specific epoxies, structural acrylics, or cyanoacrylates combined with primers is crucial to achieve reliable bonding.






Leave A Comment