Ever wonder what keeps your car’s engine from freezing in the dead of winter or overheating in the scorching heat? Or how industrial coolants and antifreezes maintain stable temperatures under extreme conditions? The answer lies in a seemingly simple yet chemically powerful compound: Ethylene Glycol (EG).
What is ethylene glycol? It is a versatile synthetic organic chemical compound. A colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting liquid, ethylene glycol (eg) might otherwise appear to be innocuous, but it has a relatively high toxicity that requires it to be handled with caution. It is a diol, a molecule with two hydroxyl groups, and as such, it possesses a combination of properties that render it highly useful in industries, especially as an ethylene glycol coolant for automotive and HVAC systems. However, the sweetness of this compound has been lethally deceptive, particularly to animals and children, such that ethylene glycol toxicity is a serious public and environmental health concern.
The Chemistry Behind the Compound: Understanding Ethylene Glycol
Chemical Formula and Structure
The ethylene glycol formula is C₂H₆O₂, and the chemical representation is HOCH₂CH₂OH. Since it is a diol, its composition consists of two hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to each carbon atom.
This simple configuration – the Ethylene glycol structure – has severe repercussions. The hydroxyl groups make EG highly reactive and water-absorbing, allowing it to easily participate in hydrogen bonding. These intermolecular forces are the premise for its efficacy as an antifreeze compound in that they disrupt ice crystal formation and lower aqueous solution freezing points.
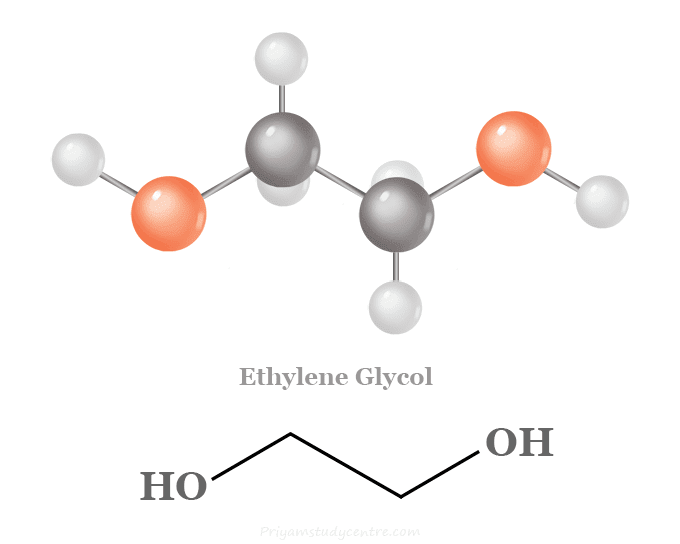
- Ethylene glycol formula: (CH2OH)2
- Ethylene glycol structure: HO-CH₂-CH₂-OH
Key Physical and Chemical Properties
The physical pinpoint properties of Ethylene Glycol make it interesting. For example, the ethylene glycol boiling point is roughly 197.3°C. This is useful because coolant systems will not over-boil during high temperatures. When mixed with water, it can significantly reduce the freezing point, which is beneficial in automotive and industrial antifreeze. Denser than water, ethylene glycol density is about 1.113 g/cm³ at room temperature. It has a higher viscosity than water and, therefore, helps lubricate mechanical systems. Also, its solubility with water allows for the mixing of homogeneous solutions, which thermal transfer fluids require.
The Ethylene Glycol Family: Mono, Di, and Tri
Ethylene Glycol doesn’t exist on its own, but it is part of a larger family, which consists of mono, di, and tri-ethylene glycols. They are oligomers produced from the reaction of ethylene oxide and water in varying molar ratios. With the increase in the number of ethylene oxide units, the molecular weight, boiling point, viscosity, and physical properties of the substance also increase. This results in different chemical properties as well as industrial applications of the derivatives of ethylene glycol.
A. Monoethylene Glycol (MEG)
Monoethylene Glycol (MEG), with chemical formula C₂H₆O₂, is the primary glycol and most manufactured and utilized. When talking about “what is ethylene glycol,” the majority of individuals are generally discussing MEG. It is a colorless, odorless, sweet, and hygroscopic liquid that is miscible with water.
Uses of ethylene glycol as MEG include its central role as an antifreeze ethylene glycol and ethylene glycol coolant in automobiles and industrial uses. Since it has a low freezing point and effective heat transferability, it protects the engine and HVAC equipment under extreme weather conditions. MEG also takes a crucial role in the production of PET plastics and polyester fibers, used in textiles, food packaging, and beverage containers.
B. Diethylene Glycol (DEG)
Diethylene Glycol (DEG), chemical formula (HOCH₂CH₂)₂O, is a product of the MEG process. More viscous and higher boiling than MEG, DEG has specialized industrial uses. DEG is hygroscopic and therefore a good humectant in uses for tobacco, printing inks, and cosmetics. The glycol antifreeze solutions may include DEG, although its use is now tightly regulated owing to ethylene glycol toxicity.
C. Triethylene Glycol (TEG)
Triethylene Glycol (TEG), or C₆H₁₄O₄, is yet another MEG derivative with a higher boiling point and stronger hygroscopicity. It is specifically discovered to be well-suited for the control of moisture. TEG is largely utilized in natural gas dehydration, where water vapor is removed from gas pipelines to prevent corrosion and hydrate formation. It is also utilized as a plasticizer in resins and air disinfectant when aerosolized, using its antimicrobial properties in commercial Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning systems.
Ethylene glycol uses
Ethylene Glycol chemicals – specifically MEG, DEG, and TEG – are found everywhere in different industries. Their chemical versatility is critical for heat transfer applications, plastic manufacture, managing moisture, and even airline safety.
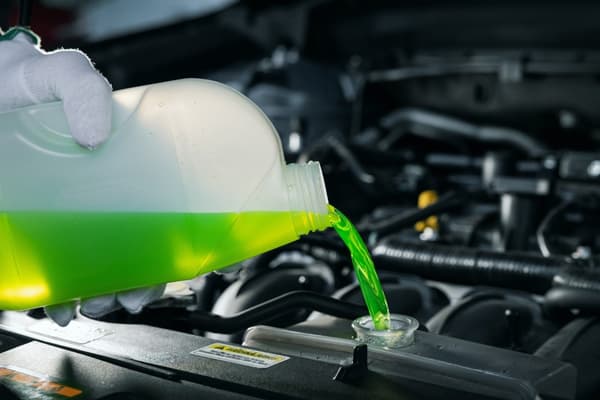
A. The Indispensable Antifreeze and Coolant
The most common use of EG is as an ethylene glycol coolant or automobile antifreeze in cars and industrial engines. They primarily use MEG in these applications. They prevent freezing in winter conditions and overheating in warm conditions by lowering the freezing point and raising the boiling point of water. The applications include automobile engines to air conditioning systems, industrial air conditioners, and heat exchangers. “Glycol antifreeze” most commonly means solutions based on MEG for such applications.

B. A Foundation for Plastics and Fibers
MEG is a key component in the production of PET plastic (polyethylene terephthalate) and polyester fibers. Through polymerization, MEG is transformed into polymers which are used in: Synthetic textiles (e.g., clothing, home furnishings), Packaging of food and beverages, and Industrial packaging and films.

C. Critical De-icing and Anti-icing Solutions
Ethylene Glycol de-icing fluids are essential to aviation safety in cold climates. MEG -and occasionally DEG – are formulated into aircraft anti-icers and runway de-icers since they depress the freezing point and stick to surfaces.

D. Other Significant Industrial and Niche Uses
Across industries, MEG, DEG, and TEG find applications as solvents, humectants, and heat transfer fluids:
- Brake fluid concentrates often make use of DEG due to its water-absorbing and viscosity characteristics.
- Inks, resins, and thinners rely on DEG to supply smooth consistency and control over drying.
- TEG’s role in the processing of natural gas offers dry gas delivery and secure pipeline operation.
- Ethylene glycol coolant blends have a significant function in efficient heat management in electronic and HVAC cooling systems.

Crucial Safety Information: Understanding Ethylene Glycol Toxicity and Risks
A. The Dangers of Ethylene Glycol: Why It’s Poisonous
Ethylene Glycol is widely used in various products, such as Ethylene glycol coolants, ethylene glycol antifreeze, and industrial fluids, but it is highly toxic. Due to its sweet taste, which is similar to that of sugar, it is highly hazardous because it leads to inadvertent ingestion, most often by pets and children. After ingestion, EG becomes metabolized by the liver into its toxic metabolites such as glycolic acid and oxalic acid.
These metabolites disturb the biochemical balance of the body:
- Glycolic acid induces metabolic acidosis, reducing the pH of the blood.
- Oxalic acid crystals precipitate out with calcium to form calcium oxalate crystals, which may inflict severe kidney damage, leading to acute renal failure.
- In addition, EG affects the central nervous system, and its symptoms range from dizziness and sleepiness to seizures and coma.
B. Recognizing the Signs: Symptoms of Poisoning
The clinical phases of ethylene glycol poisoning progress neurologically for some time, indicating: one can act drunkenly while speaking with incoherence, feeling queasy and lightheaded, even seizure-like in its manifestations within the initial framework of half an hour to some hours. This can be attributed to the nervous system’s glycolic acid and EG disturbance. Eventually, one could define further phases: an additional breath-sustaining stage and renal stage through the course of a day, up to 72 hours.
This advanced stage showcases symptoms that are rest-related, with concern towards an increase in heart rhythm, hypertension or a variation of it, breathing disorders, lack of oxygen and moisture, along with an active pulse. All of these could reflect pronounced CP phase syndromes, on a CV foundation, through re-inhaled CO2, producing even further stagnation, surfacing a progressive acidosis. Worsening conditions can be described as a lack of functioning kidneys, provoking pain near the waist area while urinating less, suffering from complete to partial grinding of the bladder alongside a total/partial cessation of fluid outflow, which can lead to organ failure. This stems from the process of creating crystals within kidney tubules.
C. Emergency Response and First Aid
Immediate treatment of suspected ethylene glycol poisoning is critical:
- DO NOT induce vomiting unless instructed by a doctor.
- Call Poison Control or your local emergency services directly.
- Rush the patient to an emergency department.
- Fomepizole or ethanol antidotes could block the conversion of EG into toxic metabolites if administered early.
- IV fluids, bicarbonate, and even dialysis can be needed.
D. Safe Handling, Storage, and Disposal
To minimize the risk of exposure and ethylene glycol toxicity, primary safety practices are necessary. Keep ethylene glycol (eg,) at all times in original packaging with child-resistant caps and clear labeling and out of the way of food and liquids so as not to be accidentally ingested. Provide proper ventilation whenever EG is being used in an enclosed space so as to prevent the inhalation of toxic fumes. In storage, keep EG products away from children and pets. In handling, utilize proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), e.g., goggles and gloves, to protect the eyes and skin. Dispose of EG products according to local environmental regulations as hazardous waste, and clean spillage immediately with containers securely covered to prevent leaks or contamination.
E. Regulatory Oversight and Public Health
Due to its danger, Ethylene Glycol is regulated by several agencies:
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversee EG safety in the workplace and industry.
- Bittering agents, such as denatonium benzoate, are added by most manufacturers to discourage consumption by making the product bitter.
- EG is a hazardous chemical regulated, and employers must distribute Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and train employees for safe handling.
Ethylene Glycol vs. Propylene Glycol: A Crucial Distinction in Safety and Use
A. Key Differences in Toxicity and Application
While Ethylene Glycol works well for automotive and industrial applications, it is extremely toxic. Propylene glycol (PG), however, is a low-toxicity alternative and is commonly used in food-grade and pharmaceutical-grade applications. PG is FDA-approved for use in things like medications, cosmetics, and even processed foods. It’s also common in theatrical fog, electronic cigarettes, and pet-safe antifreeze. In contrast to EG, PG is safely metabolized by the human body and is appropriate for use where direct or incidental human contact is required.
B. When to Choose Which Glycol
Select Ethylene Glycol when performance is crucial:
- Best suited for automotive coolants and industrial heat transfer fluids, as well as systems with low freezing and high thermal efficiency needs.
- Found in products such as glycol antifreeze and Ethylene glycol coolant. Avoid EG and choose propylene glycol (PG) when a concern of toxicity arises.
- Suggested for food-processing plants, pharmaceutical production, and pet-safe antifreeze.
- Critical in places where unintentional consumption or exposure to skin will occur.
Environmental Considerations of Ethylene Glycol
Ethylene Glycol is also believed to be biodegradable, but its emission into the environment, especially aquatic ecosystems, has major negative impacts. In large quantities, it can cause water pollution by lowering the oxygen levels, which in turn kills aquatic life. Dumping of any type of ethylene glycol, such as used ethylene glycol antifreeze or coolant, can result in chemical spillage polluting the soil and groundwater. In addition, Ethylene glycol poisoning extends as far as ecosystems and not just animal or human well-being. It is degraded by microbial activity in water treatment plants, but overloading water treatment plants has risky consequences. Safe disposal in approved waste centers is required to minimize the environmental impact and prevent ethylene glycol poisoning of wildlife. Promoting awareness and adherence to environmental policies ensures safe use and disposal of this valuable but risky chemical.
Conclusion
Ethylene Glycol is the lifeblood of industries – from coolant and antifreeze to manufacturing solvents – and thus it becomes a basic necessity. In order to know the Ethylene glycol uses and the types of ethylene glycol is important to utilize its application while minimizing hazards. Though of such broad usage, ethylene glycol toxicity and the danger of ethylene glycol poisoning require precautionary safety precautions. Safe handling, proper storage, and proper disposal are not to be compromised aspects of wise utilization. Industrial and public awareness of chemical safety is essential to preventing unwanted exposures and environmental risks. Let us foster sound decision-making and public knowledge through the dissemination of this information, cultivating a safety and responsibility culture in EG management.
